Deepfake technology has gained popularity over the years. Whether it’s deepfake audio, video, or an ad campaign for good, the innovation has been the talk of the table. Shockingly, 71% of people still need to learn about the term deepfake.
Let’s understand from the start what a deepfake is, its types, its positive and negative uses, and its detection to prevent digital malice.
What is deepfake?
Deepfake comes from combining “deep learning” and “fake.”
It refers to synthetic media that changes existing content by swapping one person’s face with someone else’s. This creates new and unique videos or audio where a person appears to say or do things they never really did.
Often, the terms deepfake and deepfake technology are misinterpreted. Let’s take a look at the basic difference between their use and meaning.
Deepfake & Deepfake Technology
Deepfake and deepfake technology refer to the same underlying concept of using the power of AI and machine learning.
The difference between them lies in how they are perceived, particularly in terms of intent and context.
Difference between Intent and Context
- Deepfake:
Intent: It is frequently linked to negative and controversial uses.
Context: It’s often used in social discussions or harmful contexts such as deepfake porn, etc.
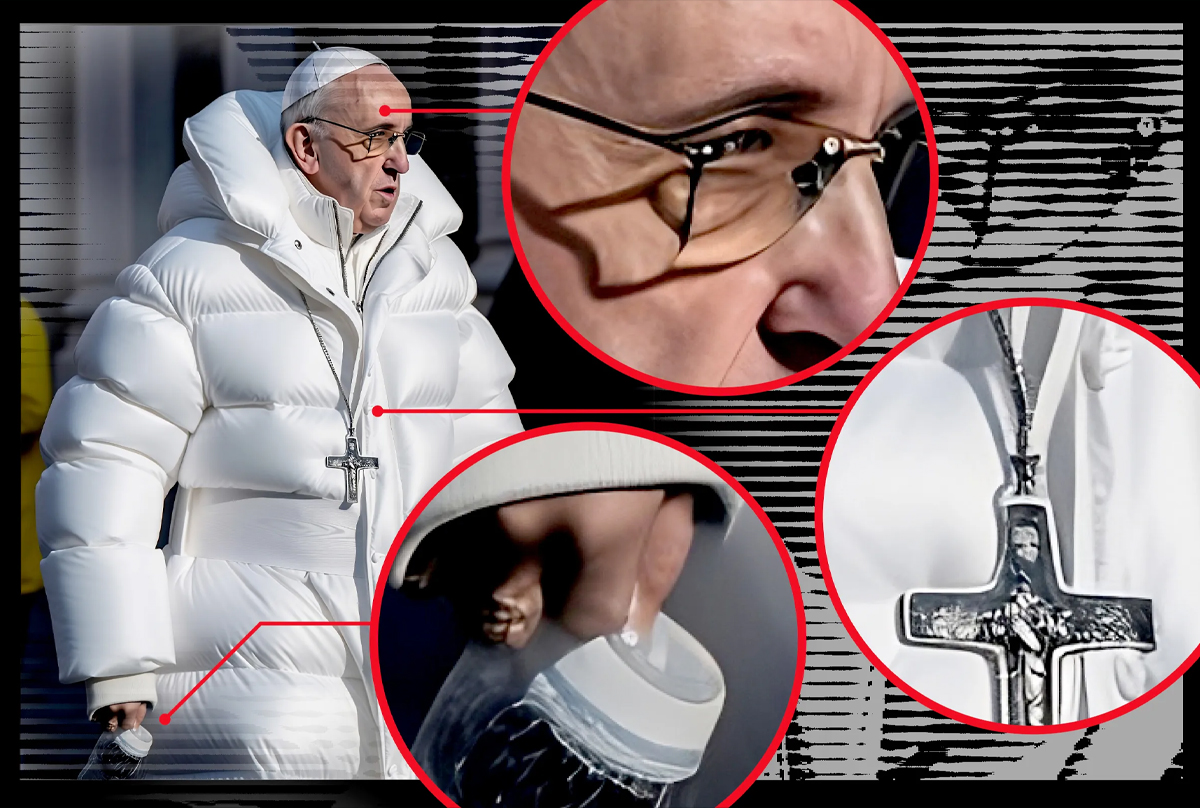

Source: image courtesy @art_is_2_inspire via Instagram
Example: The deepfake image of Pope Francis in a trendy Balenciaga coat went viral. This sparked talks about the thin line technology creates between real and fake.
- Deepfake Technology:
Intent: The term deepfake technology is associated with positive uses. It focuses on its innovative and technical uses across industries such as academia, medicine, and music.
Context: The term deepfake technology is used in technical, professional, and academic discussions focusing on the use of technology.
Example: A notable example is the video featured in the Malaria Must Die Campaign. The deepfake video features David Beckham speaking in nine different languages.
Therefore, we can understand that both terms are interchangeable depending on the use and context. Deepfake technology emphasizes the technical part, and the deepfake highlights the end product.
Similarly, deepfake has a diverse effect on society. It has the potential to make a positive impact as well as a negative one. But all of this depends on how humans perceive technology and its uses.
Before we focus on the pluses and minuses of the technology, it’s necessary to see how deepfake creates real faces to fake.
How does Deepfake work?
Deepfake uses a form of AI called ‘deep learning’ to create synthetic media. This involves complex data collection, analysis, model training, and image manipulation.
Making a high-quality deepfake video is more challenging than it sounds. It applies different AI mechanisms, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Recurrent Neural Networks.
GAN is a commonly used AI deep learning technique for deepfakes. They favored it due to the highly realistic fake images and videos.
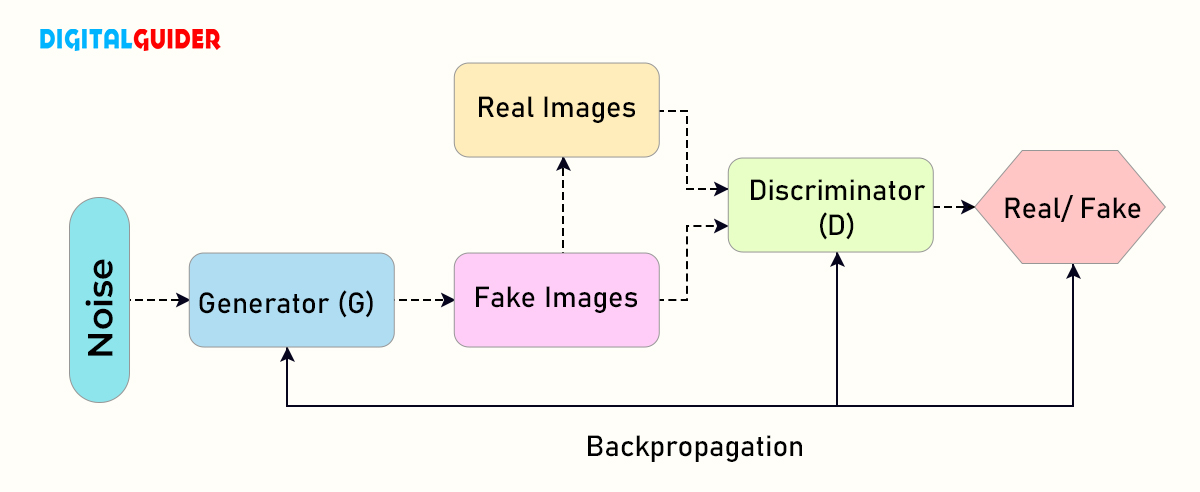
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
GAN is a new neural network to produce fake images that look as real as possible.
Well, GAN consists of two neural networks:
- The generator: This neural network generates images. It acts like an artist trying to produce fake media.
- The Discriminator: The discriminator neural network detects whether the image created is fake or real. It acts as a critique.
WeGAN is a repetitive process. The generator improves at producing convincing fake content, and the discriminator becomes more adept at spotting fake content.
Types of Deepfakes:
Various forms of deepfakes are involved, from face swap to gesture manipulation and hybrid deepfakes (combining multiple techniques). But, as technology improved, it is categorized into three main parts:
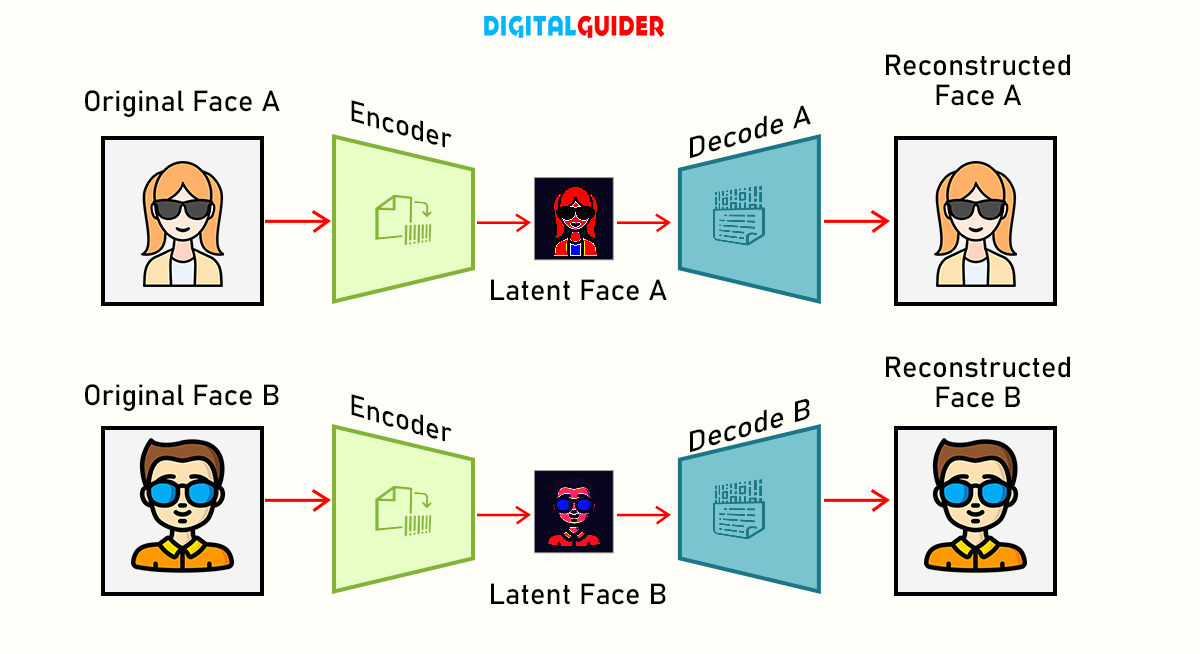
→ Face Swaps:
Face swap is the most common form of deepfake. A new face image replaces the main subject image through AI and deep learning.
Phone apps like Face Swap Live, TikTok, Cupace, and Snapchat are the easiest ways to change from real to fake. They can be used for still images, videos, and live streams.
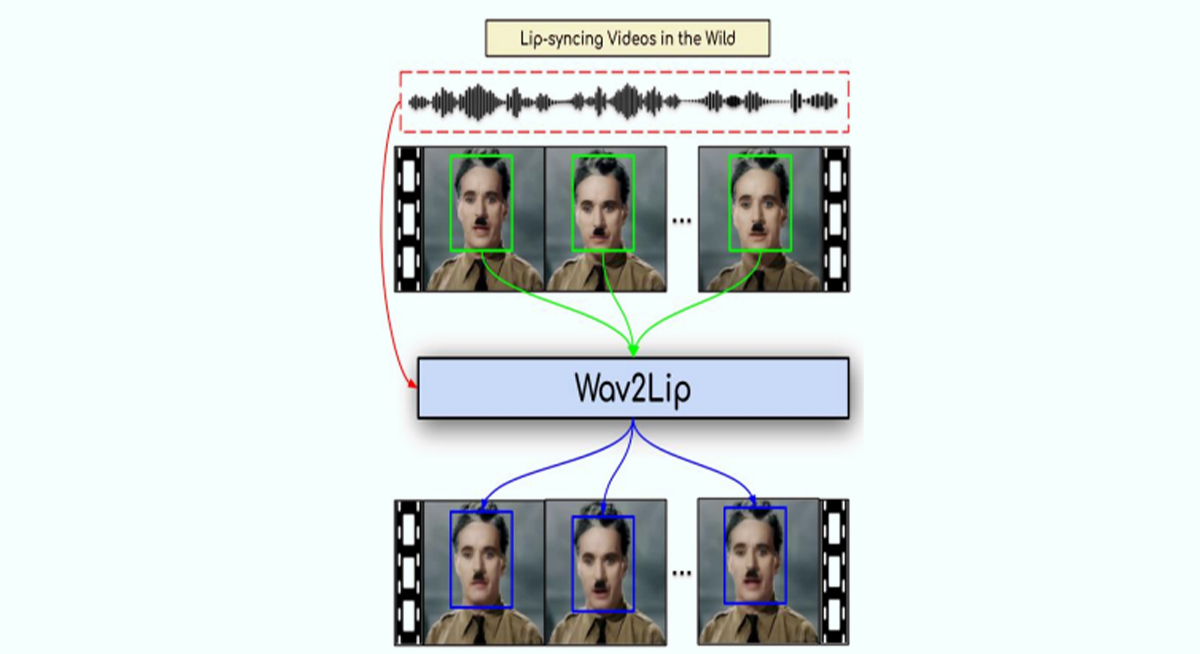
→ Lip Sync:
In a lip sync deepfake, the subject’s voice is altered and appears to speak new content. It involves voice mapping to make the video subject seem more authentic. Lip-syncing technology uses recurrent neural networks (RNN); this RNN model allows a third party to put words in the mouths of celebrities and famous figures.
A new AI technology, WAV2Lip, has made lip sync deepfake creation more accessible and convenient. It can dub movies, translate lectures, and perform live translations at press conferences.
Source: dhs.gov
—The main features of WAV2Lip
- Works for any face
- Highly accurate for the videos that are out there (in the wild video)
- Works for any language
- Works for synthetic voices
→ Puppet deepfake:
Puppet-master deepfake is one popular and modest method of making deepfake. It is also known as the re-enactment technique. The puppet deepfake technique uses GAN.
In this deepfake technique, the person in the source video controls the facial expressions and movements of the person in the target video or image.
Uses of Deepfake Technology
While deepfakes have raised concerns as a digital threat, they also hold significant potential for positive and legitimate uses in various industries.
Let’s look at the positive and negative uses of deepfake technology.
– Positive uses of deepfake
Audio and Entertainment:
Deepfake technology is very vividly used in the audio and entertainment industries.
Disney made the earliest use of deep learning technology. It is used in all film industry sectors, including production, content creation, voice modulation, and dubbing.
Example: Star Wars used deepfake techniques for Princess Leia and Grand Moff Tarkin.
- Advertising and marketing:
Deepfake advertising has been significantly impacting the world for a while now. It offers advantages such as personalizing ads, creating models with desired ethnicity and characteristics, generating content, and reaching a wider audience.
Education and training:
Deepfake technology plays a pivotal role in the education industry, enhancing practical understanding among students and contributing to better learning outcomes.
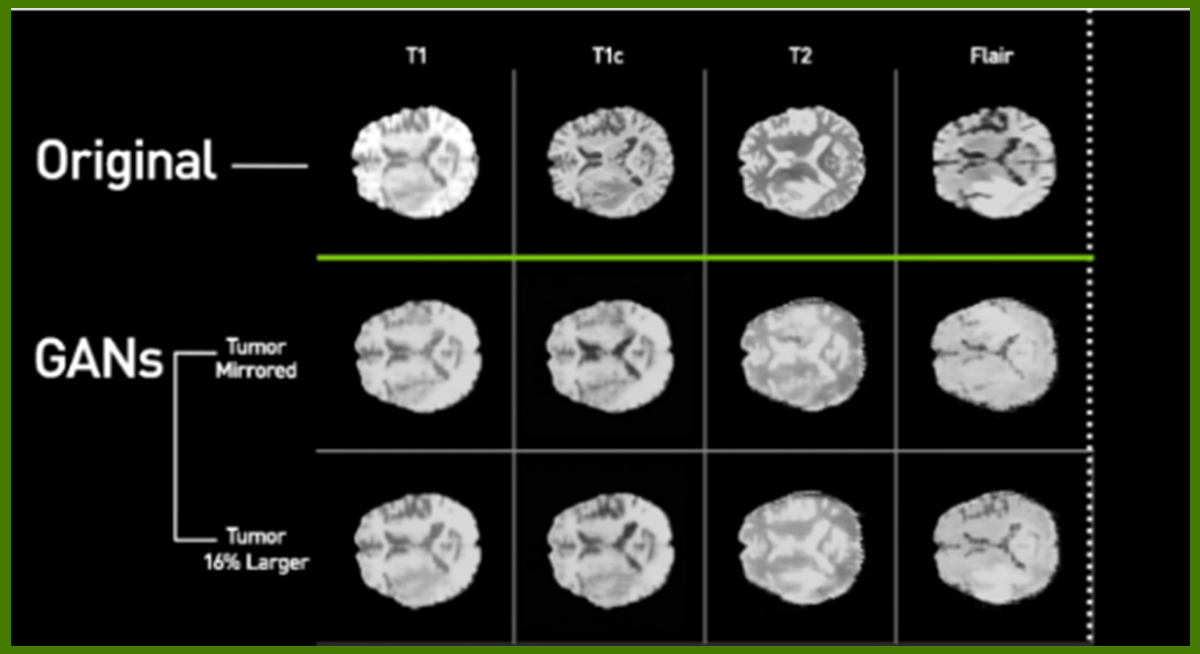
Source: Image courtesy Shin et al.
In the medical field, deepfake is used for research and teaching. GAN neural networks can produce artificial brain MRI images, aiding cancer detection and training. Its potential in healthcare can reassure the audience about its positive impact on healthcare and education.
Legal:
In a legal setting, deepfake is used in two ways:
Firstly, deepfake technology helps identify deepfake videos through detection software.
It helps to verify the authenticity of the digital content and prevent the manipulation of evidence.
Secondly, it is used to enhance the video quality and to restore the evidence in a criminal investigation.
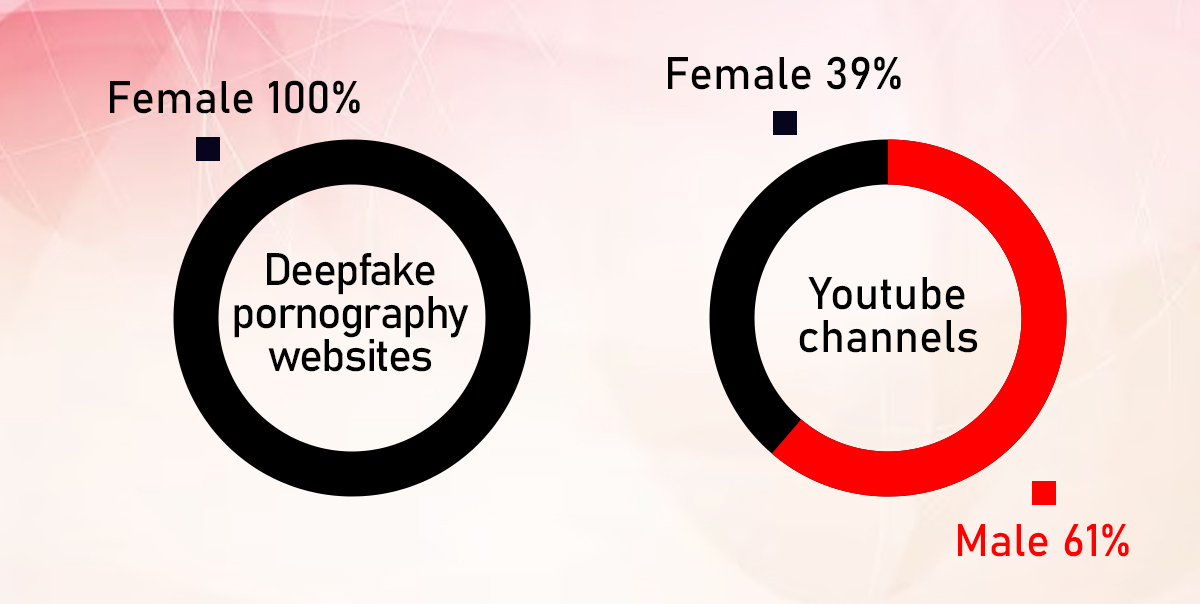
Of all the available deepfake videos, it contained 96% of the pornographic material. The deepfake incidents affected several female celebrities, including Emma Watson, Gal Gadot, Scarlett, etc.
Scams/Phishing:
Deepfake phishing is a cybercrime. A malicious actor uses an algorithm to fabricate video, audio, or image content that appears to be authentic, which favors them.
Deepfake phishing can be seen in various types, such as emails, video calls, voice messages, etc. It poses a significant threat to email security. To prevent deepfake phishing, organizations should use AI threat detection programs to recognize and report scams.
Identity theft:
Deepfakes are a severe form of identity theft. It can result in financial loss and reputational damage.
Deepfake technology can create and steal new identities of real personalities. The attackers use the technology to create fake faces, voices, and documents to make people fall prey to their intentions.
It has created a threat among consumers of all ages, especially the older generation. Threats like unauthorized access to bank accounts can damage trust in online identifications and other banking systems.
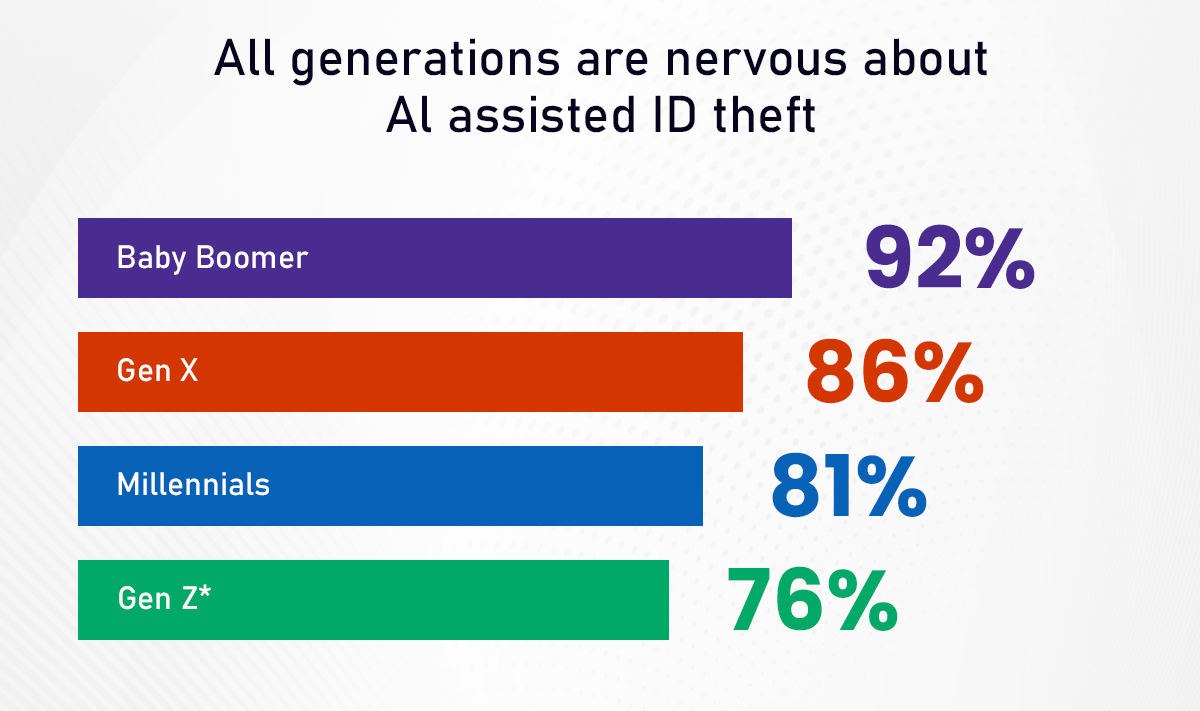
Stats from Nationwide
How to Detect Deepfake Content?
Deepfake detection has become challenging as the content becomes better and more realistic. Detectors can struggle with the large amount of synthetic online content, but there are ways to detect fake content.
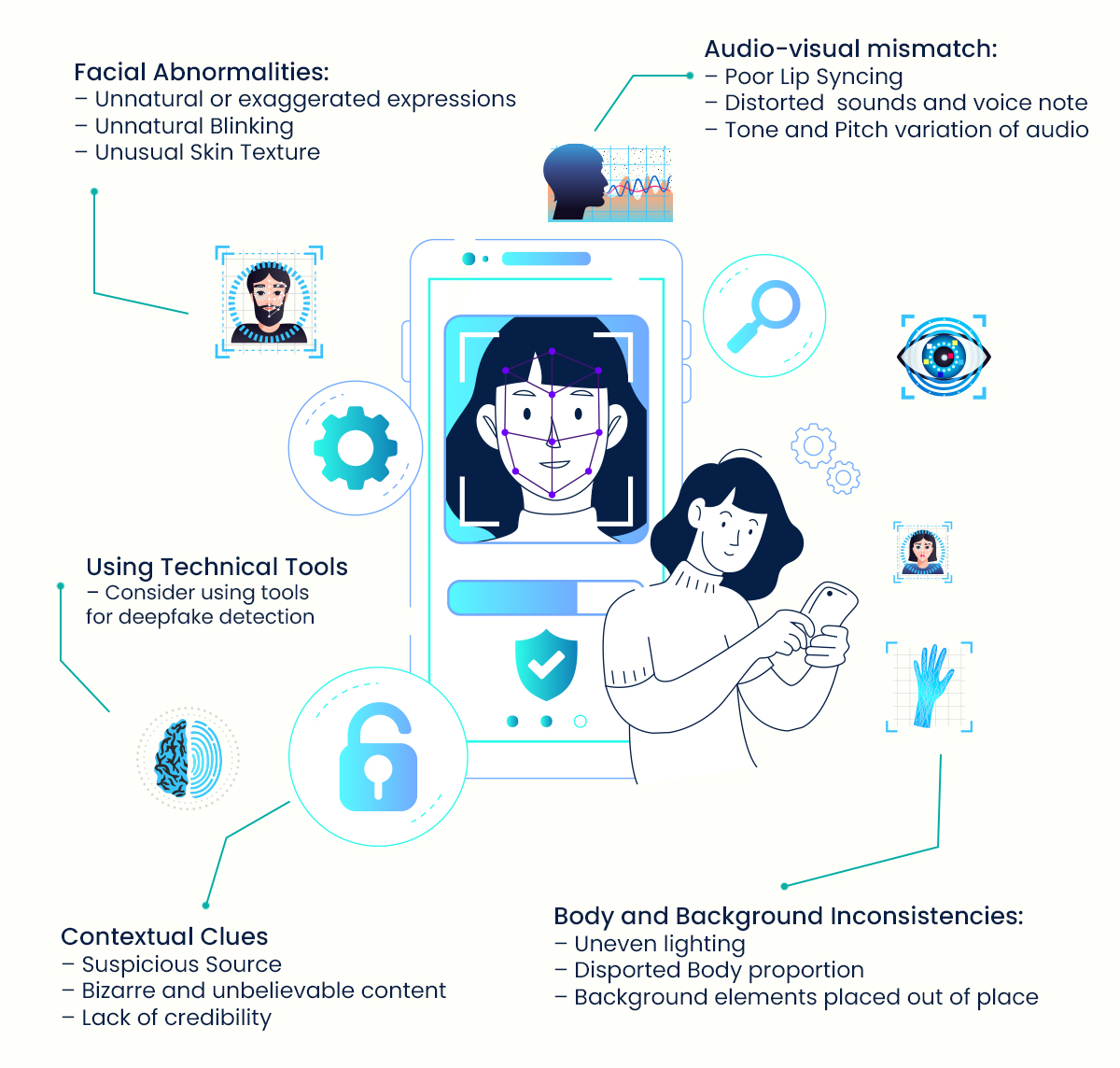
- Facial Abnormalities:
– Unnatural or exaggerated expressions
– Unnatural blinking
– Unusual skin texture
- Body and Background Inconsistencies:
– Uneven lighting
– Distorted body proportion
– Background elements placed out of place
- Audio-visual mismatch:
– Poor lip-syncing
– Distorted sounds and voice notes
– Tone and pitch variation of audio - Contextual Clues:
– Suspicious Source
– Bizarre and unbelievable content
– Lack of credibility - Using Technical Tools:
– Consider using tools for deepfake detection.
Conclusion
Deepfake technology is a blessing in disguise. It enables different industries to use it as an asset while posing significant ethical and social challenges.
Deepfake uses in society raise questions about how technology is used. They evoke a balance between innovation and moral responsibility. Positive uses should be regulated, and malicious uses should be detected to mitigate risk and ensure the responsible use of AI in the digital age.







