What is “People Also Search For” (PASF)?
People Also Search For (PASF) is a dynamic Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) feature that displays 6-8 related search queries users commonly look for after performing an initial search. It helps users refine their queries when initial results don’t fully match intent, acting as Google’s suggestion: “Didn’t find what you need? Try these.” These are phrase-match or semantically similar terms derived directly from Google’s massive search database. You’ll usually see PASF appear when a user clicks a result reflecting real user behavior to infer that the user is still searching for better or clearer information. PASF excels for topical authority—queries cluster around your pillar content.
Not every query shows PASF. It depends on volume & trends. It is evolving with AI Overviews (AIO). You will note its rise in SERPs, pushing organic results lower.
How PASF Works
Google’s PASF analyzes:
User behavior:
Queries from users who searched your term and refined it (e.g., bounce-back signals after quick returns to SERP).
Search patterns:
Historical data, location, device (mobile/desktop), and searcher history.
Semantic intent:
Similar topics, long-tail variations, or modifiers.
Difference between ‘People Also Search For’ & ‘People Also Ask’
Both People Also Search For (PASF) and People Also Ask (PAA) are Google SERP features designed to help users refine searches and discover related information. However, they serve distinct purposes, appear under different conditions, and provide different types of suggestions. These features remain core to Google’s user experience, especially with AI-enhanced search.
PAA: Focuses on answering related questions directly on the SERP with expandable snippets.
PASF: Suggests alternative keyword phrases (not questions) for users who didn’t find what they needed.
Here is a side-by-side comparison:
| Aspect | People Also Ask (PAA) | People Also Search For (PASF) |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Expandable questions with short answer snippets | List of 6-8 related keyword phrases clickable links that start a new search |
| Content Type | Questions (“What is the best seo tool?”) | Non-question phrases (“best free tools”). |
| Trigger | Appears immediately at the top of the most SERPs | Appears when you click a result and quickly bounce back to the SERP |
| Location | Usually mid-SERP and infinite scroll with more questions | Under the clicked result (desktop) or mid/bottom (mobile) |
| User Interaction | Expand for answer; load more questions. | Click to perform a new search |
| SEO Opportunity | Rank in snippets: direct traffic + visibility | No direct ranking, but it informs content for topical authority. |
| Example | “What are the best SEO tools?” (expand for snippet). | “best free SEO tools”, “SEO tools for beginners”. |
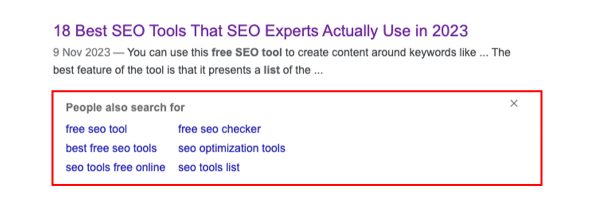
‘People Also Search For’ (PASF) results:
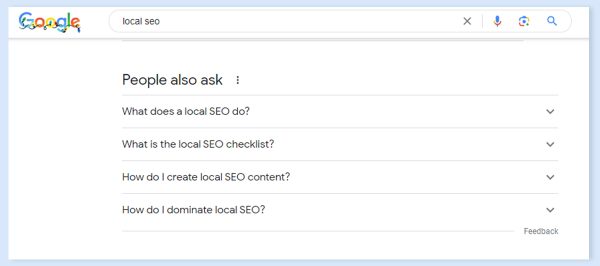
‘People Also Ask’ (PPA) results:
How to Optimize for ‘People Also Search For’
‘People Also Search For’ is a great way to improve your Search Engine Optimization, help your business get more visitors, and improve the user experience. The AI-driven search era is dominated by GEO (Generative Engine Optimization), and AEO (Answer Engine Optimization). Nowadays, Google uses ML and behavior signals to leverage SEO. In the AI era, ranking isn’t about answering the first question; it’s about anticipating the next one. PASF shows you that next step. People Also Search For is one of the most powerful tools for building high-intent topic clusters. PASF reflects real user behavior, making it a direct signal of a search.
“Suppose your business sells skincare, haircare, and salon services, and you want to rank on those keywords. However, you’re not targeting the user’s search intent. When you get PASF keywords such as ‘Keratin Treatment for Oily Hair,’ ‘On Location Hair & Make-up services,’ ‘Men’s Hair Grooming,’ or ‘Skin Tanning Removal,’ you can easily create a pile of content around these relevant searches.”
Why PASF matters for SEO in the AI Era
- “People Also Search For” is built entirely around real human behavior, i.e., what users click, what they find unsatisfying, and what they search next. PASF captures authentic query chains straight from Google’s user signals. In an AI-driven search, LLMs prioritize behavior over keywords.
- “People Also Search For” data reveals user intent, showing where users get stuck and what information they are missing. For example, a search for “SEO for Doctors” might surface related queries such as medical SEO pricing, local SEO for clinics, and HIPAA SEO compliance. AI interprets this broader context and provides relevant information.
- Another advantage of optimizing for “People Also Search For” is its ability to reduce pogo-sticking (a behavior where users quickly click back and forth) between search results because they don’t find the information they need. AI-driven systems closely monitor this to provide effective PASF to keep users engaged.
- In the AI era, People Also Search For has become core to building topical authority. Google now rewards pages that demonstrate topic depth, cover concepts thoroughly. PASF data reveals semantically connected topics, missing subtopics, and identifies natural opportunities for internal linking.
- Another strong reason to optimize for PASF is its alignment with AI Overviews and Search Generative Experience (SGE). These AI-generated answer pages, which incorporate PASF topics, demonstrate comprehensive coverage, making them far more likely to be cited and pulled into AI summaries. By building content around PASF, you may compete for modern AI-driven search results.
- AI-era SEO is built around content that adapts to how users think and search in real time. ‘People Also Search For’ bridges this gap by identifying the user behavior after their initial query. A single search may expand into multiple, related information blocks. Instead of optimizing for one “perfect” answer, PASF enables multi-layer answer that aligns with user behavior.
- PASF helps you add relevant sub-sections and answer the natural “what next?” questions that often cause users to leave. On service pages—where conversion matters most—PASF can guide the creation of supporting pages, strategic internal links, and intent-driven content that moves users closer to a decision. For ongoing optimization, refresh older posts with PASF topics.
How to extract PASF keywords
- Search your target keyword in the search bar
- Click a top-ranking result
- Hit the back button
- Copy the PASF terms that appear
- Alternatively, you can use tools like Keywords Everywhere, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Nightwatch AI agents
- Analyze PASF Keywords for search volume, intent, trend, etc.
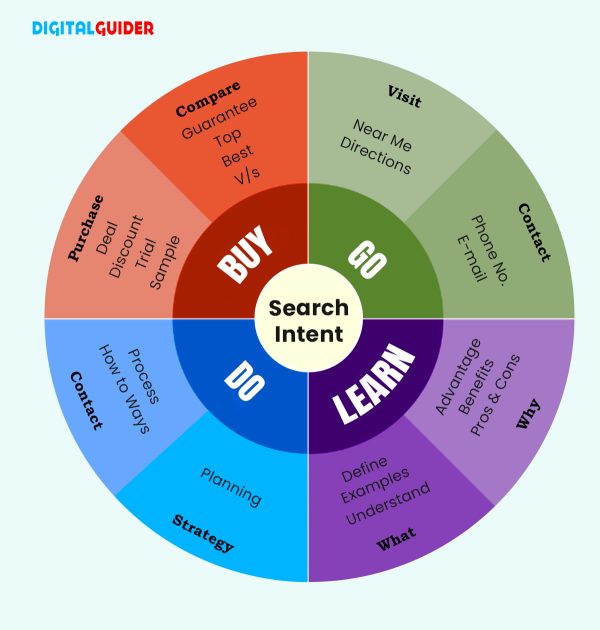
Types of Search Intent
Search intent refers to the purpose or aim of the user who is searching or navigating through the search results, from quick tasks to deep research. It could be a home remodel or funny videos. Google’s end goal is to satisfy a user with its results and to end the search. For that, it provides suggestions in the form of People Also Search For (PASF). This helps a user quickly browse other searches with similar intent and get what they want to know ASAP.
Navigational searches involve users looking for a specific landing page or website. These searches are common when users are familiar with a brand or website and want quick, direct access without navigating through general search results. It’s akin to entering a specific address into a GPS; the goal is a straightforward journey to a known location. In such cases, People Also Search For often surfaces closely related brand names, login pages, or official resources to help users reach the exact destination faster.
Informational:
Informational searches are driven by users seeking awareness of a particular topic. In this intent, users are curious and want to gather knowledge. The primary aim is to acquire information. Examples include looking up historical events, understanding scientific concepts, or researching a hobby. Here, People Also Search For (PASF) expands the learning journey by suggesting follow-up questions and related subtopics users commonly explore next.
Commercial:
Commercial searches signify users conducting research before making a purchase. In this intent, users are exploring options and comparing products or services. These searches often involve terms like “best,” “reviews,” or “compare,” etc. Understanding commercial search intent is crucial for tailoring content that positively addresses users’ research and influences their purchasing decisions, while People Also Search For helps surface alternative products, comparisons, and evaluation-focused queries.
Transactional:
Transactional searches represent users at the final stage of the buying journey, ready to complete a purchase. This intent is action-oriented, with users using keywords like “buy,” “order,” or “checkout.” The focus here is on making the desired transaction. Businesses must optimize for transactional intent by ensuring a seamless purchasing process and a clear call to action, while People Also Search For (PASF) may highlight closely related products, pricing options, or purchase variations before the final decision.
Content Strategy: Build PASF-driven topic clusters
- When you’re running out of ideas, PASF suggests fresh content ideas. Simply look up your desired topic and identify its associated PASF keywords. Open each PASF keyword in a separate tab and examine the top-ranking pages to discover fresh and distinctive content concepts. The primary benefit of using PASF keywords for content ideas is enhancing your site’s topical authority.
- You can create many new pillar pages around the topics in the PASF box, as shown in the image below. This leads to improved rankings for additional keywords associated with your niche.

- PASF keywords are particularly well-suited for FAQs, as they represent the subjects your audience is already actively searching for. Enhance your FAQ section with PASF suggestions, making it attractive to search engines. Adding FAQs at the end of your articles is a simple and engaging way to connect with your audience and boost search rankings.
On-Page SEO Improvement
- Boost your ‘on-page’ SEO by naturally incorporating PASF suggestions. To make a more search-engine-friendly website, use PASF keywords in your content. Write down relevant PASF keywords and smoothly add them to your content where they make sense.
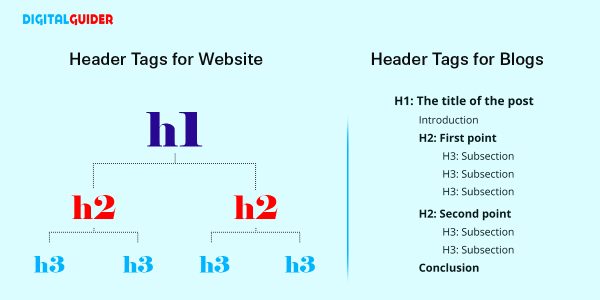
- Include PASF keywords in H2 and H3 tags for a better on-page SEO approach.
TL;DR
One of your best free resources for content ideas and website improvement is the “People Also Search For” (PASF) section. These suggestions can guide you in finding keywords, topics to write about, or questions to address. It’s like a treasure of information and can boost your SEO ranking.
Exploring this area would be smart next time you’re stuck for keywords, an outline, or content ideas. This article aims to better understand the PASF box and how it can benefit your SEO, PPC, and content marketing efforts.
FAQ – People Also Search for
A1. Because PASF is triggered by user dissatisfaction. If many users click a link and quickly return, Google assumes the result didn’t meet intent.
Q2. Can PASF keywords reveal content gaps my competitors haven’t covered yet?
A2. Yes, PASF often shows niche follow-up queries that top-ranking pages haven’t addressed.
Q3. Should I build entire pages around People also search for keywords?
A3. If a PASF keyword answers a unique question or shows strong intent, build a dedicated page or section.
Q4. Can PASF keywords help me understand micro-intents within my niche?
A4. Absolutely. PASF results often expose narrower layers of intent, helping you segment your content strategy more precisely.
Q5. Can I optimize my chatbot or site search with PASF keywords?
A5. Yes! Add PASF queries to your chatbot’s FAQs or internal search suggestions to mirror real-world user behavior.
Q6. Why do PASF results vanish when I revisit a keyword later?
A6. PASF is session-triggered. It appears only after clicking a result and bouncing back.
Q7. How often should I update my content with new PASF keywords?
A7. Every 2–3 months, updates help you stay ahead of trends, search engine updates, and shifting user intent patterns.