Is your website targeting the same keyword across multiple pages?
Your website could be unknowingly competing with itself in Google search results.
If your rankings are flatlining or key pages are underperforming, cannibalization SEO might be the silent killer sabotaging your efforts. But here’s the good news– with the right tools and smart SEO strategies, this issue can be both identified and fixed before it hurts SERP rankings.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the essentials to help you regain control of your rankings:
- What is keyword cannibalization in SEO
- Difference between Keyword cannibalization, content overlap, and duplicate content
- Common causes and how to spot them
- Methods to identify cannibalization
- Proven strategies to fix SEO cannibalization chaos
Let’s dive in—starting with the basics: what is keyword cannibalization in SEO, and why should you care?
What is Keyword Cannibalization?
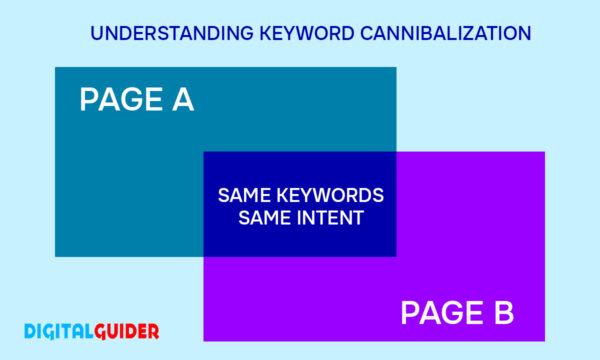
Keyword cannibalization is an SEO issue that can happen due to two reasons: when two or more pages of a website Target the same keyword and a similar search intent.
To put it simply:
The term Keywords Cannibalization or Cannibalization of keywords refers to the competition among different pages or links within the same website. This competition happens when those pages or articles are optimized for identical or closely related keywords.
It is an unintentional SEO issue that happens when your website grows and content accumulates. When several pages revolve around the same topic or keyword, it confuses Google, splits your traffic, and weakens your overall SEO performance.
| For example: There are two pages (say: A & B) from the same website (say: xyz.com) Page A: “Top 10 SEO tools for beginners”
Page B: “Free SEO tools for new business holders”
Result? |
What is the difference between keyword cannibalisation, content overlap, and duplicate content
Keyword cannibalization, content overlap, and duplicate content are often confused as similar in practice and understanding.
Although these terms may appear similar in practice, they impose major differences, and keyword cannibalization is not the same as content overlap and duplication.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between keyword cannibalization, content overlap, and duplicate content:
Issues | What it Means | Problem Caused |
Keyword Cannibalization | Multiple pages targeting the same keyword and search intent on your site | Pages compete in SERPs, diluting ranking power. |
| Content Overlap | Different keywords, but same topic or search intent. | Confuses users & search engines, weakens SEO. |
| Duplicate Content | Identical or nearly identical text on multiple pages. | Triggers content devaluation or gets ignored. |
✅ So, What Should You Watch For?
Now that you know the difference between keyword cannibalization, content overlap, and duplicate content, it’s time to focus on keyword cannibalization—when your website competes with itself, and understand when it truly hurts your SEO.
When Is Keyword Cannibalization a Problem — and When Is It Not?
Keyword Cannibalization Is a Problem When– it can impact your site’s performance
- One page is outperforming the other, yet it’s not the one you desire.
- Both pages are performing inadequately.
- The click-through rate (CTR) and traffic are below expectations.
- You’re receiving impressions but not attracting clicks.
- You’ve diluted backlinks and keyword signals across several URLs.
Keyword Cannibalization Is Not a Problem When- it doesn’t hurt your organic search performance and produces multiple pages for a reason
- A single page is performing effectively and achieving your SEO objectives.
- The two pages focus on different locations
- Every page is optimized for a diverse array of keywords.
- There is little overlap, and no adverse effects on rankings.
- You maintain robust internal linking and a well-defined topical organization.
🔍 Now that you understand what keyword cannibalization is and why it’s a problem, let’s explore the common causes behind it — and the solutions to fix them effectively.
Causes of Keyword Cannibalization
As we have understood the problems associated with keyword cannibalization, it is understood that it is rarely intentional.
Or it could have been affected due to the laid-back or outdated SEO tactics like keyword stuffing and one keyword pages, content duplicacy, etc, which is often the result of oversight.
Here are the common causes of keyword cannibalization-
Poor Content Strategy
Content publishing without a clear plan and effective SEO strategy can result in multiple pages covering similar topics or unintentionally targeting the same keywords.
| Solution: Make a content calendar or an Excel spreadsheet and match each topic with specific keywords and user intent. |
Lack of Keyword Mapping
Keyword mapping is important for planning your content strategy. Without it, different pages on your website can unintentionally compete with each other for the same keyword, confusing both Google and your audience.
| Solution: Use keyword mapping tools like Ahrefs or Semrush to assign one primary keyword per page, ensuring each page has a unique focus and avoids unnecessary overlap. |
Overlapping or Repetitive Content
Multiple pages on a website covering similar topics, especially blog posts or product pages, can compete for the same keywords and can cause cannibalization due to overlapping intent or topics.
| Solution: With regular content auditing and content merging, deleting or consolidating overlapping articles. |
Uncoordinated Content Strategy Across Teams
When marketing, SEO, and product teams generate content separately, several pages can be unintentionally optimized for the same keywords.
| Solution: Aligning the team with a shared content brief for a more parallel content strategy. |
Re-optimizing pages without redirecting to the old version
Updating or rewriting content and releasing it as a fresh page without redirecting from the previous one leads to two conflicting URLs.
| Solution: Use redirects like 301 from the outdated to the newer one |
Improper internal linking
When several pages are interlinked/ interconnected using identical anchor text (for instance, “top SEO tools”), Google might interpret that they all aim for the same keyword and lead to Search engine confusion
| Solution: Diversify anchor text and link contextually to the most relevant page for each topic. |
E-commerce Filters or URL Parameters
Dynamic URLs generated via filters or faceted navigation (such as size, color, price) can create numerous identical pages competing for similar keywords.
| Solution: setting rules in robots.txt, using canonical tags, and avoiding indexing unnecessary filter combinations. |
These key causes are often unintentional, but they directly impact your SEO health. From confusing search engines to weakening the page authority, keyword cannibalization can lead to several performance issues —
Let’s look at the major effects your website might suffer.
- Drop in search rankings
Competing pages confuse the search engine, causing a lower ranking in results.
- Reduced Click-Through-Rate
With multiple similar listings, users are less likely to click, reducing your overall CTR.
- Decreased Organic Traffic
Splitting relevance between pages leads to a decline in overall search traffic.
- Weakened Page Authority
Avoid building strength on a single page, authority is spread thin across many.
- Weakened link strength
Links from other websites tend to lose impact when divided among several similar pages.
How to Identify Keyword Cannibalization in Your Website
Before fixing cannibalization, it is essential to identify it. Here are two simple ways to find out if your site has pages competing for the same keyword:
- Manual Keyword Cannibalization Check
- Tool-based Keyword Cannibalization Check
Manual Keyword Cannibalization Check
Google Search Trick
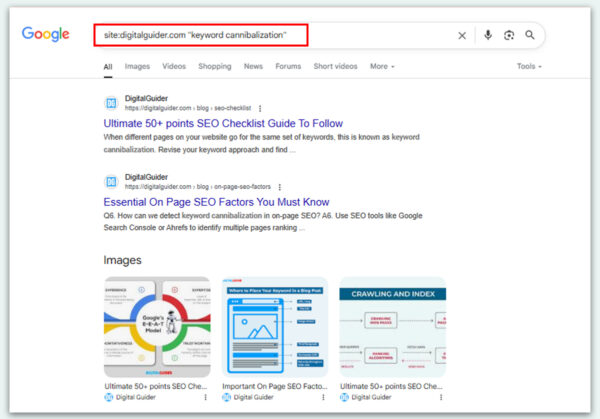
Start with a site search by using the search function site:yourdomain.com “keyword” in Google to surface all pages relevant to a particular term.
For example, A simple site search using your domain along with a keyword will display all the pages that are ranked for that specific term.
let’ s type the function- site:digitalguider.com “keyword cannibalization”
Although it’s nothing to be alarmed about, if you see many pages in the results, it doesn’t mean they all rank for the same keyword. It just shows that search engines have indexed those pages and found the keyword mentioned in them.
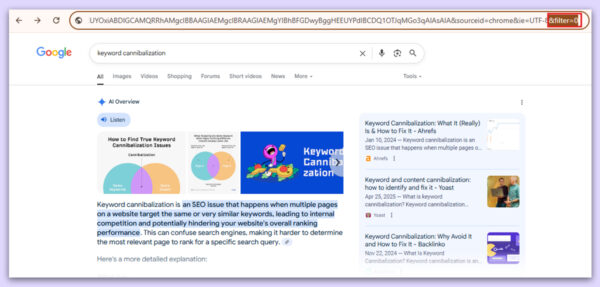
The “&filter=0” function search
By default, sometimes Google hides similar pages in search results. Adding the function “&filter=0” tells Google to show all results, even the ones typically masked in searches.
These are the unbiased search function, which provides a clear picture of the website and gives a real-time insight into the pages that might be competing for similar keywords in SERP results.
For example: Add the function “&filter=0” at the end of the URL of your particular search query.
Tool-based Keyword Cannibalization Check
Google Search Console (GSC)
Google Search Console (GSC) is a reliable tool for identifying cannibalization of keywords. It can be done with some easy steps.
-Open the GSC tool
-Navigate to Performance- Search results
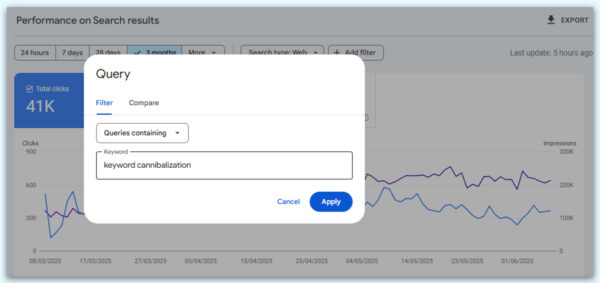
-Click to add a filter and choose the query
– Type the desired keyword
– To see all the variations of the keyword, click on the “Queries”
– Click on “Pages” to see the impressions & clicks
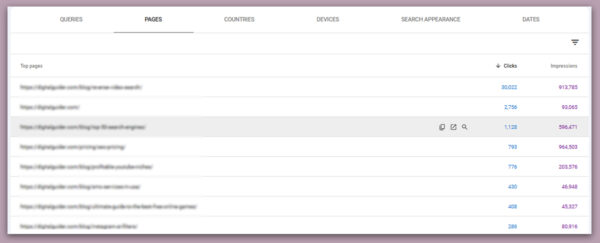
By using the data from GSC, you can plan your content strategy by understanding which pages should be redirected, consolidated, or revamped based on their performance.
Semrush
Semrush can be a great help to your website in identifying the keywords competing with each other on the same website. Here are some simple steps to follow.
- You will need an active premium subscription plan to access the full suite of SEO tools.
- Go to the “Position Tracking” tool, and select the Cannibalization Report. This will highlight if multiple pages from your site are competing for the same keywords.
- Filter the result by URL, keyword, or ranking position to pinpoint overlapping content. Semrush even grades your site’s cannibalization health, making it easier to prioritize fixes.
- Once cannibalization issues are identified, you can use Keyword Overview to refine your content strategy
In addition to Semrush, tools like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, and TrueRanker can also help you identify and make relevant changes to the cannibalised content.
Thus, streamlines the process and protects your site from SEO performance drops caused by cannibalised content.
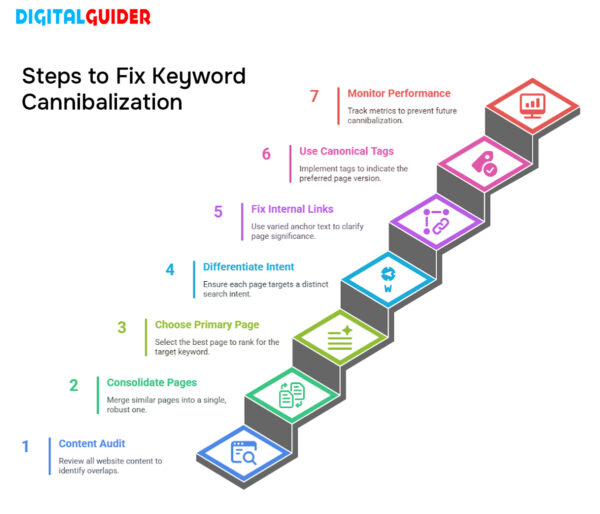
7 Key Steps to Fix Keyword Cannibalization
Identifying cannibalization on your website is the first step toward protecting your rankings and reclaiming your authority in search results.
There’s no need to panic — here are the most effective steps to fix keyword cannibalization and strengthen your SEO:
Step 1: Conduct A Thorough Content Audit
Review all the content on your website from the keyword to the intent. For an easy audit process, use a spreadsheet or SEO auditing tools, such as Semrush, GSC, or ScreamingFrog, to properly catalogue your URLs, focus keywords, and existing rankings with minimal time.
Pro Tip: Group your content by keyword themes to understand which ones overlap. Look for duplicate or very similar content targeting the same keyword.
Step 2: Consolidate Competing Pages
If two or more pages are aiming for the same keyword and presenting the same content, merge them into a single, more robust, and thorough page.
Pro Tip: Use a 301 redirect (or moved permanently HTTP status code) to send visitors from old pages to the main page, thus helping keep your link value.
Step 3: Choose a Primary Page
Decide the page you want to rank for the target keyword. This will be considered as your primary or “canonical” page for that subject.
Pro Tip: While choosing your primary page, consider pages with better backlinks, traffic, or conversion potential. It the stronger candidate to retain and can be optimized further.
Step 4: Differentiating Keyword Intent
Ensure that every page on your site has a distinct purpose and targets a different search intent — whether it be informational, transactional, navigational, or commercial—based on thorough keyword research.
Pro Tip: Use long-tail or secondary keywords to change the focus of pages and match them with different steps of the user journey (for example, “how to pick SEO tools” instead of “best SEO tools for beginners”).
Step 5: Fix Internal Links
Internal links inform search engines about which pages hold significance. When several pages interlink with identical anchor text, it creates confusion for search engines.
Pro Tip: Link contextually using varied and specific anchor text.
Step 6: Use Canonical Tags
In cases of similar or nearly identical content, implement a canonical tag to indicate the preferred version to search engines.
Pro Tip: Add (link rel=”canonical”) to in the <head> of the duplicate pages to avoid indexing issues.
Step 7: Monitor SEO Performance
After applying fixes, keep tracking keyword rankings, traffic, and engagement metrics for the affected pages. Keyword cannibalization may resurface as you introduce new content.
Pro Tip: Use position tracking tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Search Console regularly to catch new overlaps.
Is Keyword Cannibalization Always a Threat?
Keyword Cannibalization- a threat- Not necessarily.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that the majority of web pages do not solely rank for a single keyword. In reality, pages that appear in the top 10 for a keyword frequently also rank for a hundred other keywords. This indicates that even if two pages on your website appear to be competing for the same keyword, they might still be benefiting your site by ranking for different sets of keywords.
📊 Let’s take a look at the study by Ahrefs based on 3 million search queries — it shows that pages ranking in the top 10 for one keyword also rank for hundreds of others, especially those in the higher positions:
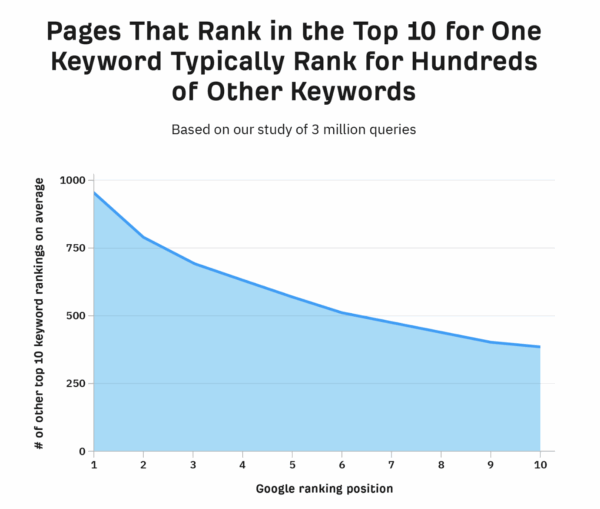
What does this mean?
👉 If two pages rank for many different keywords, removing or merging them just to “fix” cannibalization might do more harm than good.
👉 You might actually lose traffic from all the other keywords those pages were ranking for.
So instead of panicking about one overlapping keyword, it’s smarter to look at the big picture: how are these pages performing overall?
TL;DR: Keyword Cannibalization – What You Need to Know (and Do) 🔍📉
As your website grows, so does the risk of unintentionally duplicating content, leading to keyword cannibalization. This happens when multiple pages target the same or similar keywords, potentially hurting your rankings instead of helping them.
What’s the risk?
When two or more pages compete for the same keyword, they split traffic, dilute authority, and confuse search engines, resulting in lost visibility.
How to detect it:
Use tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or even a simple Google search trick to spot overlaps.
Why does it happen?
- Similar or overlapping content
- No clear keyword-to-page mapping
- Disjointed SEO efforts across teams
How to fix it:
Merge duplicate pages, assign unique primary keywords, implement redirects, and optimize your internal linking strategy.
The outcome?
Clearer keyword targeting, improved rankings, and more relevant organic traffic.
FAQ- Keyword Cannibalization
Can keyword cannibalization affect paid search (PPC) campaigns?
Yes, it can lower Quality Scores and increase CPCs if landing pages compete for similar search terms.
Is keyword cannibalization a penalty from Google?
No, it’s not a penalty—but it can harm your rankings if not managed properly.
How often should I check my site for keyword cannibalization?
At least once every quarter or during major content audits.
Can long-tail keywords help prevent cannibalization?
Yes, targeting more specific long-tail keywords reduces overlap and improves clarity.
Is cannibalization more common in large websites?
Absolutely. The more pages you have, the higher the risk of unintentional overlap.
Can internal linking fix cannibalization alone?
Not entirely. It’s helpful, but often needs to be paired with merging or redirecting pages.
Should I delete cannibalized pages?
Only if they provide no unique value. Prefer merging or redirecting over deleting.
Can keyword cannibalization hurt brand consistency?
Yes, inconsistent messaging across pages may confuse both search engines and users.
Does targeting the same keyword in blog and product pages cause cannibalization?
It can, unless the intent and structure of both pages are distinct.
Can schema markup help in resolving cannibalization?
Yes, it adds clarity to page content and helps Google understand page’s purpose better.