Search engines have come a long way from matching exact keywords. Today, Google focuses on understanding the intent and meaning behind every search. That’s where Semantic SEO comes into play—it helps your content get discovered, not just by keywords, but by the ideas and context it represents.
Semantic SEO is the practice of optimizing content around meaning, context, and entities—rather than just keywords—to align with how search engines understand language.
To put it simply, semantic SEO ensures that your content speaks the same “language” as search engines.
Example: Imagine you search for “apple”. Do you mean the fruit 🍎 or the tech giant Apple Inc. 💻?
Thanks to semantic search, Google can figure that out based on the words around your query and your past behavior.
This ability to understand context is exactly what makes semantic SEO powerful for higher rankings.
What is Semantic SEO?
At its core, Semantic SEO is about creating content that answers searchers’ questions in the most meaningful and contextually accurate way. Instead of stuffing keywords, it focuses on:
Entities → the people, places, things, or concepts your content talks about.
Relationships → how those entities connect.
Context → the intent behind a search and the environment in which it happens.
In simple words, semantic SEO tells Google “what your content really means” rather than just “what words it contains.”
The Meaning of Semantic Search in Google
Google introduced semantic search with the Knowledge Graph and Hummingbird update, shifting from exact-match keywords to understanding intent. This means:
If someone searches “best running shoes for flat feet”, Google won’t just look for pages with the phrase “running shoes.”
Instead, it will prioritize content that explains shoe types, foot conditions, and expert recommendations.
Traditional SEO vs. Semantic SEO
Traditional SEO → Optimize for one keyword at a time (e.g., “best SEO tools”).
Semantic SEO → Optimize for the topic as a whole (e.g., covering “SEO tools,” “keyword research,” “competitor analysis,” and “on-page optimization” together).
👉 This shift matters because it builds topical authority. When your content covers a subject in depth and connects all the right entities, Google starts recognizing your site as a trusted source.
Why Semantic SEO is Important in 2025?
Search behavior is evolving—and so are search engines. People no longer type in robotic phrases like “SEO tips 2025.” Instead, they ask natural, conversational questions like:
“How can I rank higher on Google without keyword stuffing?”
“What’s the best SEO strategy for AI-driven search?”
This change means Google isn’t just matching words—it’s interpreting intent. That’s where Semantic SEO becomes a game-changer.
The Rise of AI & Conversational Search
With Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), ChatGPT browsing, and voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, search is becoming more like a conversation.
Users expect direct, context-rich answers.
Search engines rely on entities, context, and relationships to serve those answers.
👉 If your content is optimized semantically, you stand a better chance of appearing in featured snippets, knowledge panels, and AI-generated answers.
Why It Matters for Rankings
Improves topical authority → Google sees you as a subject expert.
Captures long-tail queries → ranks for multiple variations, not just one keyword.
Boosts engagement → content feels more natural, answering user intent.
Future-proof SEO → aligns with how AI and semantic search are evolving.
💡 Think of Semantic SEO as building a library, not just a bookshelf.
Instead of one keyword = one page, you create clusters of content that cover an entire topic in depth, signaling authority to Google.
How Semantic SEO Works?
To understand how semantic SEO works, think about how Google processes information. It doesn’t just scan for words—it tries to understand meaning, intent, and connections the way a human would.
Here are the key elements that power semantic SEO:
Entities, Context & Relationships
Entities: Distinct things like “Apple Inc.,” “Steve Jobs,” or “iPhone 16.”
Context: The words, phrases, and searcher’s intent surrounding an entity.
Relationships: How entities connect (e.g., “Steve Jobs → Co-founder → Apple Inc.”).
Google uses its Knowledge Graph to map these relationships, which helps it decide which result best fits a search query.
LSI Keywords vs. Semantic Keywords
Many people confuse LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords with semantic keywords. They aren’t the same.
LSI Keywords: Related terms that appear in similar contexts (e.g., SEO → search engine optimization, ranking, backlinks).
Semantic Keywords: Words that define meaning & intent (e.g., “how does semantic SEO help AI search engines?”).
👉 Pro Tip: Use tools like Google NLP API, SurferSEO, or LSI Graph to find semantic keywords that strengthen your content.
Role of Schema Markup in Semantic Search
Schema markup gives search engines a structured way to read your content.
Example: If your blog has an FAQ section, adding FAQ schema tells Google these are questions & answers → increasing chances of a featured snippet.
Sample JSON-LD snippet:
| { “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is Semantic SEO?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Semantic SEO is the practice of optimizing content around meaning, context, and entities—rather than just keywords.” } }] } |
Semantic SEO works by combining entities, context, and structure (schema) to help Google “understand” your content and rank it higher for both keywords and intent-based queries.
Strategies to Implement Semantic SEO
Knowing what semantic SEO is isn’t enough—the real power lies in putting it into action. Here’s a step-by-step framework you can follow:
1. Optimize Content with Semantic Keywords
Don’t just focus on one keyword. Build topic clusters around related entities.
Use semantic variations (e.g., for Semantic SEO, include semantic markup, entity-based SEO, and latent semantic indexing keywords).
Tools to try:
Google “People Also Ask” → discover intent-based questions.
LSI Graph & SEMrush Topic Research → expand semantic coverage.
2. Use Schema Markup & Semantic Tags
Add structured data: FAQ, Article, HowTo, or Product schema.
Use semantic HTML tags like
<article>,<section>,<header>,<footer>.Example: Mark up your blog FAQs so they can appear in rich snippets.
3. Improve Internal Linking for Context
Link related pages together → builds topical clusters.
Example: From this blog, link to:
LSI Keywords Guide
Schema Markup SEO
Anchor text tip: Use contextual anchors (“semantic tags in SEO” instead of “click here”).
4. Create Comprehensive Topic Hubs
Publish pillar content (in-depth guides) + supporting blogs.
Example:
Pillar: “Semantic SEO Guide 2025”
Supporting blogs: “What are LSI Keywords?”, “How Schema Markup Improves Rankings,” “Entity SEO Explained.”
This signals topical authority to Google.
5. Monitor & Optimize with AI Tools
Use Google Search Console → track semantic queries you’re already ranking for.
Try AI-driven SEO tools like SurferSEO or MarketMuse → analyze semantic gaps.
Regularly update your content to stay relevant with new search patterns.
Tools for Semantic SEO
Using the right tools can make semantic optimization faster and more accurate. Here’s a curated list of tools that help you identify entities, semantic keywords, and content gaps.
1. Google NLP API (Free)
Purpose: Analyze text for entities, sentiment, and syntax.
Why Use It: Helps understand how Google interprets your content semantically.
Use Case: Detect entities in your blog and ensure you cover all relevant topics.
2. LSI Graph (Freemium)
Purpose: Find LSI keywords related to your main topic.
Why Use It: Expands your content to include semantically related terms naturally.
Use Case: If your main keyword is Semantic SEO, LSI Graph suggests related phrases like semantic markup, latent semantic indexing, and semantic tags.
3. SurferSEO (Paid)
Purpose: Provides content optimization based on semantic relevance.
Why Use It: Analyzes top-ranking pages and suggests related terms, headings, and keywords to improve topical authority.
Use Case: Compare your blog with top-ranking competitors and fill content gaps.
4. Clearscope (Paid)
Purpose: Helps create semantically rich content by recommending related terms and concepts.
Why Use It: Ensures your content covers the topic comprehensively for Google’s semantic understanding.
Use Case: Optimize blog content by adding semantic keywords naturally.
5. SEMrush Topic Research (Freemium)
Purpose: Discover popular subtopics and questions users are searching for.
Why Use It: Gives you ideas for content expansion and FAQs.
Use Case: Find long-tail queries to integrate into your blog for semantic coverage.
Comparison Table (Quick Overview)
| Tool | Type | Use Case | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google NLP API | Free | Entity & sentiment analysis | Free |
| LSI Graph | Freemium | LSI & semantic keyword research | $ |
| SurferSEO | Paid | Semantic content optimization | $$ |
| Clearscope | Paid | Semantic keyword & topic coverage | $$ |
| SEMrush Topic Research | Freemium | Topic & subtopic discovery | $–$$ |
💡 Pro Tip: Start with free tools to identify entities and LSI keywords. Use paid tools for in-depth semantic content optimization when scaling your SEO efforts.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Semantic SEO
Even smart content can get buried if you miss these!
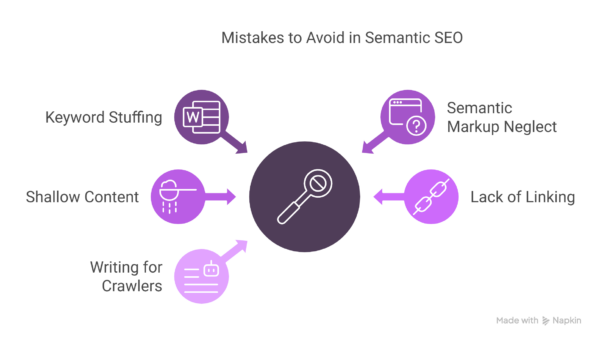
1. Over-optimizing with Keywords (Even LSI Ones)
Yes, LSI keywords and semantic keywords are important, but stuffing too many can feel forced. Remember, Semantic SEO is about flow and context, not cramming in every related term.
✅ Do this instead: Use LSI keywords naturally within answers, subheadings, and examples—where they genuinely fit.
2. Ignoring Semantic Markup Structure
If you’re still using generic <div> everywhere and skipping semantic elements like <header>, <article>, or <footer>, you’re missing out on serious SEO clarity.
Google loves a well-structured semantic markup landing page because it makes the content easier to crawl, index, and rank.
✅ Use proper HTML5 semantic tags to organize your page visually and contextually.
3. Not Matching User Intent Fully
If your content only scratches the surface of a keyword, without diving into the “how” and “why,” you’re likely to get outranked by sites that go deeper.
Example: For a query like “semantic search meaning”, answering just the definition isn’t enough. You also need to cover:
- How it works
- Its role in Google’s algorithm
- Why it matters for SEO
✅ Cover the full context behind a search, not just the literal query.
4. Weak Internal Linking (Or None At All)
One isolated blog post won’t help you build topical authority.
If you’re not linking between related topics, like:
- latent semantic indexing keywords
- SEO semantic markup
- LSI SEO Strategies
…you’re leaving a lot of ranking power on the table.
✅ Create clusters and connect your content with relevant anchor text.
5. Writing for Bots, Not Humans
Google’s algorithms are smart now. If your content reads like it was written by a machine or just to please a semantic search engine, users will bounce, and rankings will drop.
✅ Keep the tone human. Write to help first, optimize second.
💡 Quick Tip:To level up your content, try this mini checklist:
|
TL;DR: Embracing a Smarter, More Human SEO
Semantic SEO is no longer optional—it’s essential for ranking in today’s AI-driven, intent-focused search landscape. By optimizing your content for meaning, context, and entities, you can:
Build topical authority that Google trusts.
Rank for multiple long-tail and conversational queries.
Increase visibility in featured snippets, knowledge panels, and voice search results.
Key Takeaway: Focus on topics, not just keywords. Cover related entities, answer real user questions, and structure your content with semantic SEO principles.
Next Step: Want to implement Semantic SEO on your website but don’t know where to start? Explore our SEO services to optimize your content for higher rankings and better search visibility.
FAQ – Semantic SEO
Q1. Can Semantic SEO help me rank for more specific, long-tail keywords?
A1. Absolutely! By focusing on search intent and related topics, you can rank for long-tail and niche keywords naturally.
Q2. Does Semantic SEO work for voice search?
A2. Yes! As voice search becomes more popular, Semantic SEO makes it easier for Google to match your content with voice search results.
Q3. How do I find the right LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords for my content?
A3. By using tools like LSI Graph or Google’s People Also Ask feature, you can find related terms.
Q4. How can I improve the search intent matching on my site?
A4. You can create content that answers the “why,” “how,” and “what” of the query.
Q5. Do I need to rewrite all my old content to implement Semantic SEO?
A5. Not necessarily. In many cases, revamping existing content by adding semantic markup and incorporating related keywords or topics can be more than enough to boost your SEO.
Q6. Can Semantic SEO improve my chances of appearing in Google’s featured snippets?
A6. Yes, by focusing on search intent, using structured data, and providing well-organized content.
Q7. What tools can I use to implement Semantic SEO on my website?
A7. Tools like Surfer SEO, MarketMuse, and InLinks can help optimize your content.
Q8. Why should I care about semantic search if I’m already ranking well with traditional SEO?
A8.Ultimately, by adapting, you can stay ahead of the curve, increase your chances of ranking for more nuanced queries, and enhance user experience.