When you build a website for your business, one of your main objectives should be ensuring it meets Google’s standards. Whether you’re a web developer, product owner, business owner, analyst, search engine optimizer, software developer, or tester, Google Lighthouse can help you identify opportunities to improve your website through easy steps with no coding skills required.
In this post, we’ll cover what is Google lighthouse, how Google Lighthouse works, and how you can use it to audit your web pages and improve your site.
Read on to learn more, or you can also partner with the best SEO professionals with years of experience and know the essentials of core web vitals.
What is Google Lighthouse?
Google Lighthouse is an open-source (meaning the community maintains it & is free to use) automated tool by Google that lets you look at your website through the eyes of Google’s algorithms.
It lets you see how well your website performs regarding technical layout and page speed.
It helps you audit the user experience of web pages and identify where your site is creating a negative experience for users and Google. For Windows, simply you’ve to click on the INSPECT option and then LIGHTHOUSE, then click the ANALYZE LOADING PAGE option to proceed with the auditing. Keep reading what is Google Lighthouse speed test is to optimize your site properly.
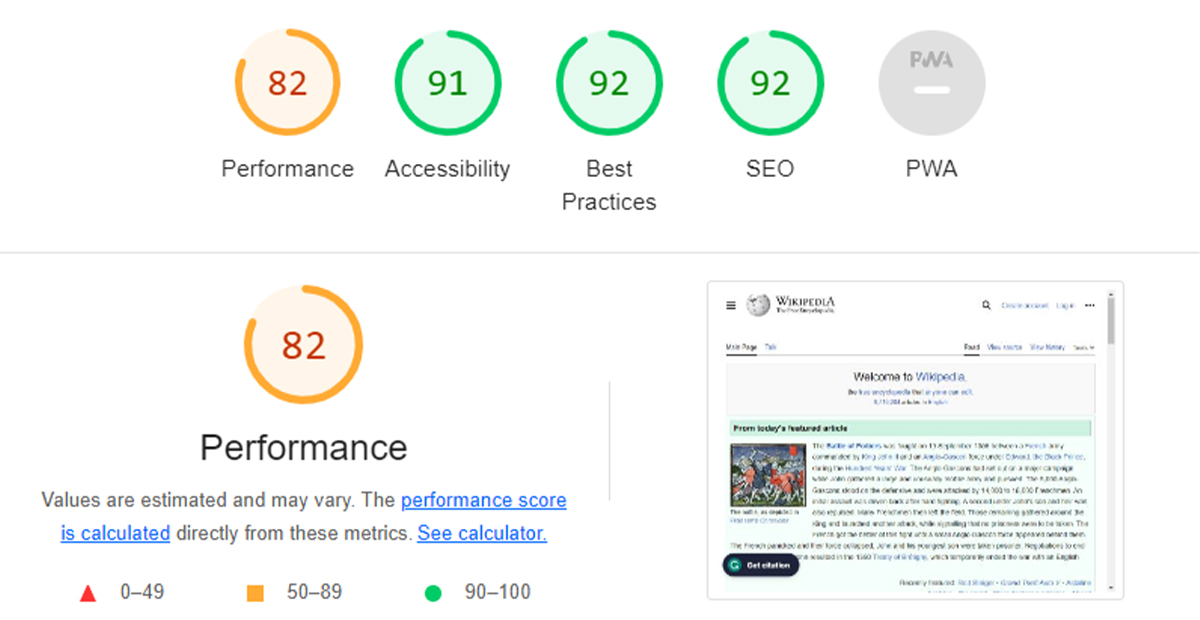
Lighthouse uses a web browser called Chromium to build pages and runs tests on the pages as they’re built.
When you run your site URL through Lighthouse, it will receive feedback on various features that may need improvement.
For example, if your page takes too long to load or isn’t mobile-friendly enough, Lighthouse will show you that.
Why does the Lighthouse matter?
Lighthouse lets you easily measure site performance across these metrics to see which areas of user experience need your attention most. You can then use these metrics to optimize site performance, accessibility, and usability to enhance SEO. This leads to increased search engine rankings > higher traffic levels > ultimately more online sales.
How Does Google Lighthouse Work?
The main focus of Lighthouse audits is to follow Google Core Web Vitals. If you’re not familiar with this, these are the essential metrics Google uses to evaluate web pages’ speed and overall UX. These Core Web Vitals consist of the (LCP) Largest Contentful Paint, (FID) First Input Delay, and (CLS) Cumulative Layout Shift.
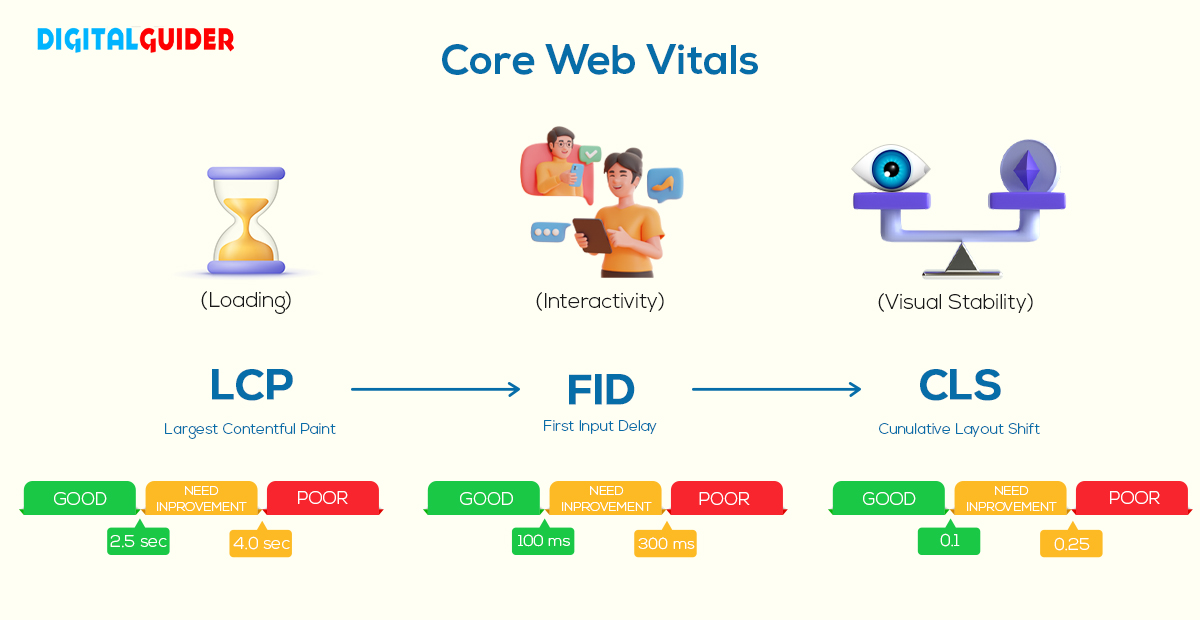
In other words, using Lighthouse assists you in seeing your website like Google does. You can apply the actionable insights it delivers to improve your pages for better search engine ranking results. Keep reading what is Google Lighthouse website test is to optimize your site properly.
Different Methods You Can Use To Run Google Lighthouse:
- Chrome DevTools: Audit pages that require authentication and read your reports in a user-friendly format.
- A Chrome extension: The extension will display a report of your Lighthouse assessment.
- From the command line: Automate your Lighthouse runs via shell scripts.
- A Node module: Integrate Lighthouse into your continuous integration systems.
- A web User Interface (UI): Run Lighthouse and link to reports without installing a thing.
Once you submit a URL to this automated tool, it will execute multiple page audits and create a specific report detailing its performance. You can then use suggestions from the results to improve your website.
What Audit Metrics Does Google Lighthouse Measure?
Google Lighthouse performs audits for five main website optimization categories.
- Performance
- Accessibility
- Best Practices
- SEO
- Progressive Web App
Google Lighthouse has a clear score scale of 1-100, allowing you to review your pages and identify where improvements can be made. You can drill down into each section to gain deeper insights, discover opportunities to enhance your page in real-time and test your pages against a realistic 3G network.
1- Google Lighthouse Performance Analysis:
Performance analysis is one of the audit categories supported by Lighthouse, along with SEO, Best Practices, and Accessibility. Each category is assigned a Google Lighthouse score from 0 to 100. In this audit, Lighthouse analyzes the speed at which a website loads and the speed at which users access the website.
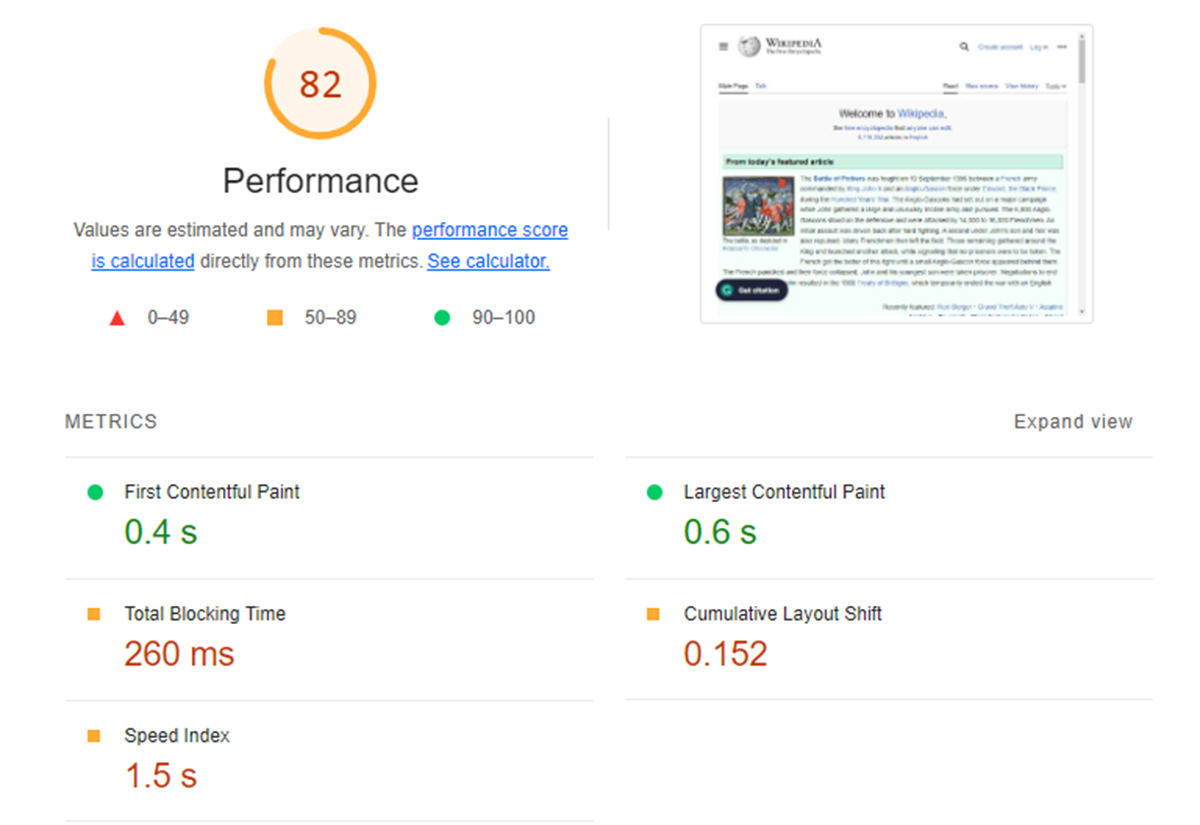
In versions 8 and 9, Lighthouse’s performance score comprises six metrics, each contributing a percentage of the total performance Google Lighthouse score.
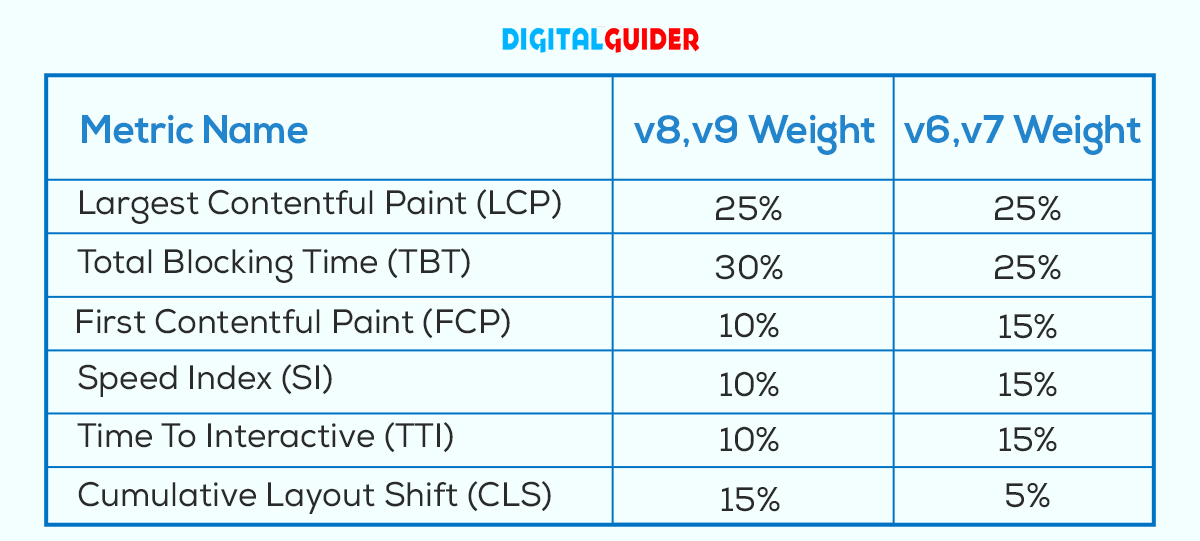
Now move on to major matrics that report your site performance, each measuring some aspect of page speed:
A- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
Calculates a page’s time to load its largest element or main web page content for users. Largest Contentful Paint is one of the three Google Core Web Vitals metrics. To improve LCP, look at the entire loading process and ensure every step is optimized. To provide a good UX, sites should strive for an LCP of 2.5 sec or less for at least 75% of page visits.
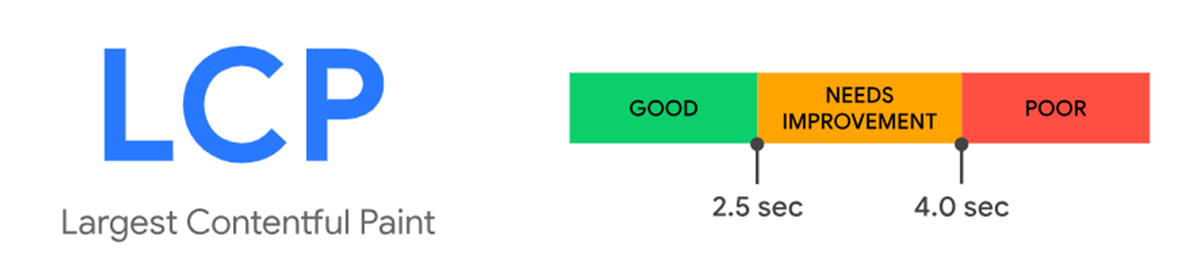
LCP is complicated, and its timing can be affected by several factors. But if you optimize LCP, then it is primarily about improving the load of the LCP resource; it can significantly simplify things. Keep reading what is Google Lighthouse score is to optimize your site properly.
Optimizing LCP can be summarized in 3 steps:
- Ensure the LCP resource starts loading ASAP & can render its resource finishes loading
- Deliver the initial HTML document as quickly as possible.
- Reduce the loading time of the LCP resource as much as you can without sacrificing site quality.
B- First Contentful Paint (FCP):
FCP (First Contentful Paint) measures the time at which the first text or image of the document object model (DOM) content becomes visible to users. As per web.dev, For this metric, “content” refers to text, images (including background images), <svg> elements, or non-white <canvas> elements.
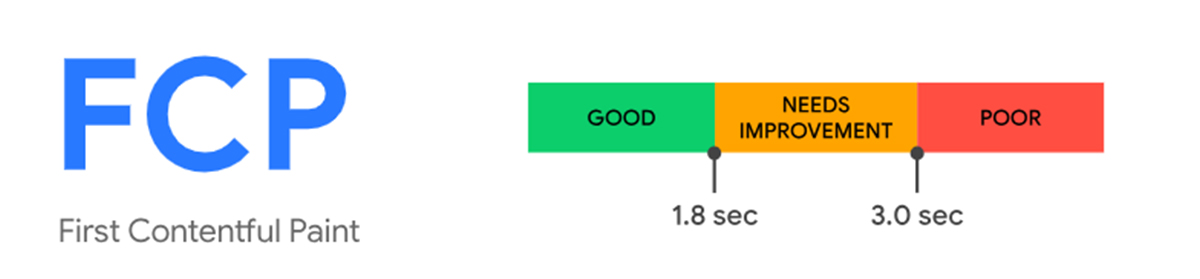
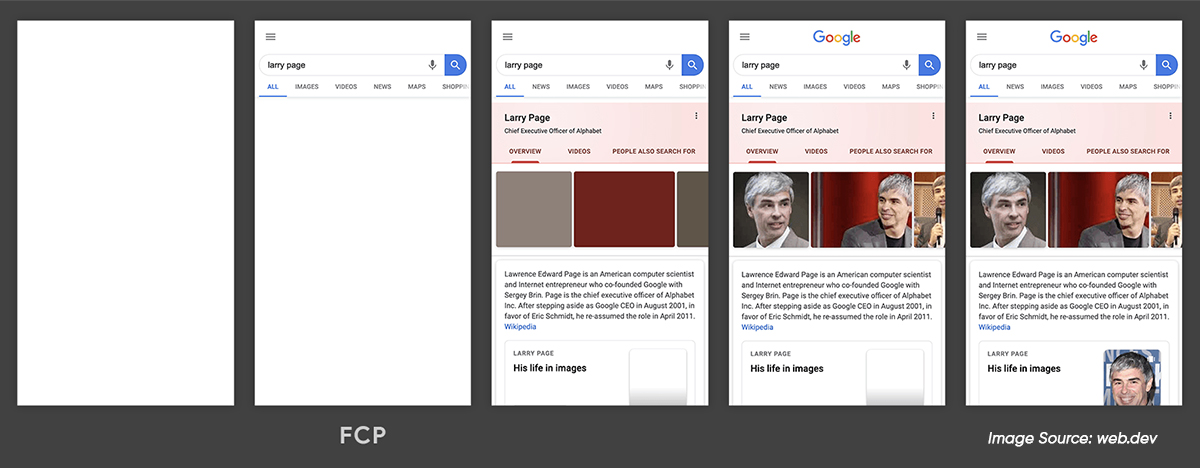
Image Source: web.dev (FCP loading timeline)
In the above image showing the loading timeline, First Contentful Paint happens in the second frame, as that’s when the first text & image elements are rendered on the screen. You can run a Lighthouse performance audit to improve it and apply any specific opportunities or diagnostics the audit report suggests. Keep reading about how does Google Lighthouse work to optimize your site properly. Moreover, you also should know how to enhance the level of content so that Google can notice it for search generative experience, which can help rank your site.
To improve FCP in general (for any site), refer to the following performance guides:
- Eliminate render-blocking resources
- Minify CSS
- Remove unused CSS
- Preload key requests
- Remove unused JavaScript
- Preconnect to required origins
- Reduce server response times (TTFB)
- Avoid multiple-page redirects
- Minimize critical request depth
- Serve static assets with an effective cache policy
- Avoid enormous network payloads
- Avoid an excessive DOM size
- Ensure text remains visible during webfont load
- Request counts low and transfer sizes small
C- Time to Interactive (TTI):
TTI measures a page’s load responsiveness and how long it takes for users to be able to click on and interact with the elements on a page. To make it interactive, the page has to display content and respond to user inputs in less than 50ms. Here are the tips to improve TTI:
- Remove or optimize JavaScript
- Avoid chaining the critical requests
- Use ‘preload’ key request
TTI is an important user-centric metric because it measures how quickly visitors can interact with your page fully. To visitors, a slow TTI can feel like your website is unresponsive, broken, or doesn’t work.
D- Total Blocking Time (TBT):
Measures when a site page is blocked from reacting to user input, such as a mouse click. It shows how unresponsive a page was before it became fully interactive. Total Blocking Time measures what’s happening between FCP (when the first text or image was painted) and TTI (how long users can click and interact). Total Blocking Time is a metric you must watch when optimizing your website’s performance.
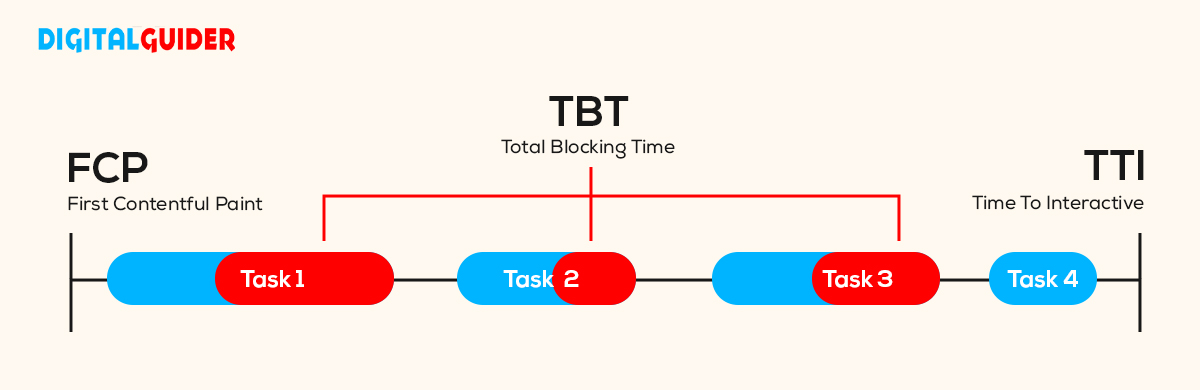
E- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
It measures the layout shifts (aka. session window) that occur as users access a page. It is a stable Core Web Vital, user-centric metric for measuring visual stability because it helps quantify how often users experience unexpected layout shifts. Layout shifts can be distracting to users. To provide a good user experience, sites should strive for a CLS of 0.1 or less for at least 75% of page visits.
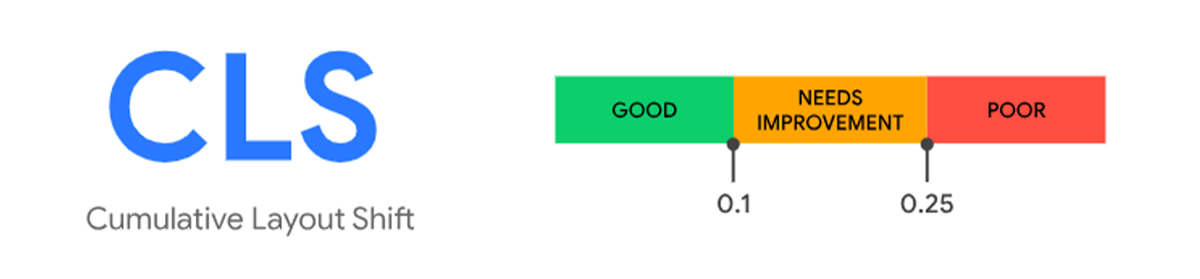
The most common causes of poor CLS are:
- Ads, embeds, and iframes without dimensions
- Images without dimensions
- Dynamically injected content such as ads, embeds, and iframes without dimensions
- Web fonts
Here in this video by Google Chrome Developers, you can learn the tips for optimizing CLS for a better user experience. Keep reading what is Google Lighthouse speed test is to optimize your site properly.
F- Speed Index (SI):
A Speed Index is a metric that measures the speed at which a page’s content is loaded. The Speed Index scores are calculated by comparing your page’s speed index with the speed indexes of actual websites based on HTTP Archive data. Anything you can do to speed up your site’s load time will increase your Speed Index, but addressing Diagnostic audits’ findings should have a significant effect. Doing this will help Google avoid unnecessary index pages if the site performs well. Here are some tips to follow:
- Minimize main thread work
- Reduce JavaScript execution time
- Ensure text remains visible during webfont load.
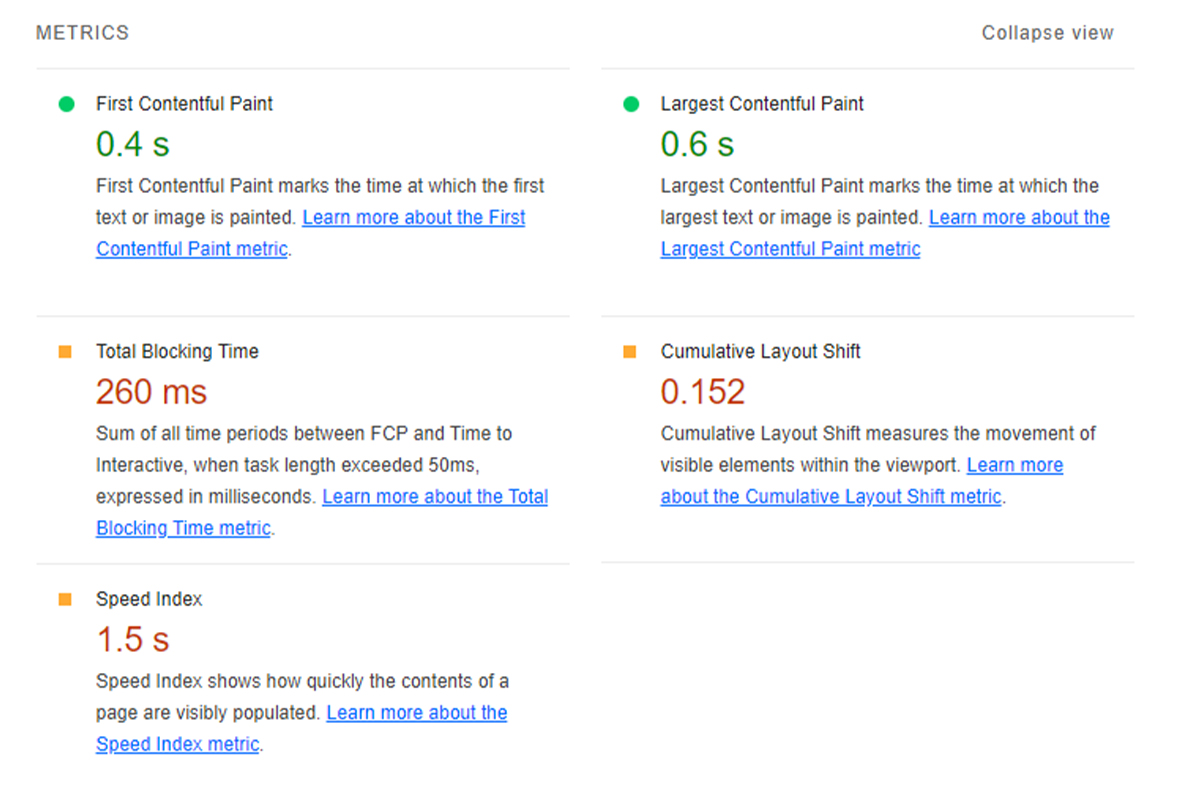
Lastly, see the below image, which shows the complete overview of how the performance report appears in a real window.
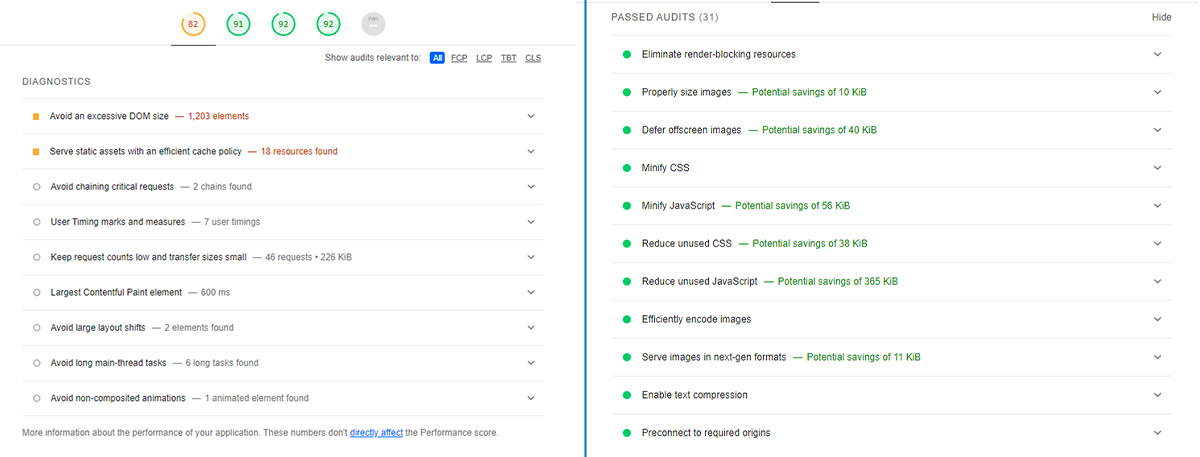
Lighthouse also provides suggestions you can implement to improve your performance, as shown in the image below.
2– Google Lighthouse Accessibility Analysis:
Next, Lighthouse assigns an accessibility rating to your page, which is a summary of how well your page is accessible to people with disabilities. Lighthouse’s accessibility test assesses how well users of assistive technologies are able to use your website. It looks at elements such as buttons and links to determine if they are adequately described.
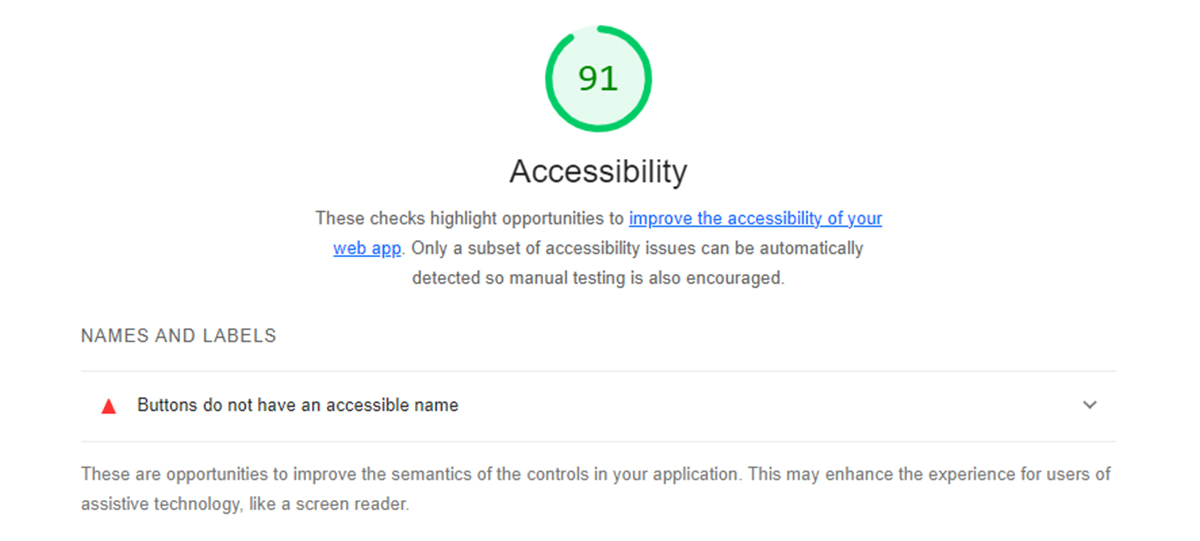
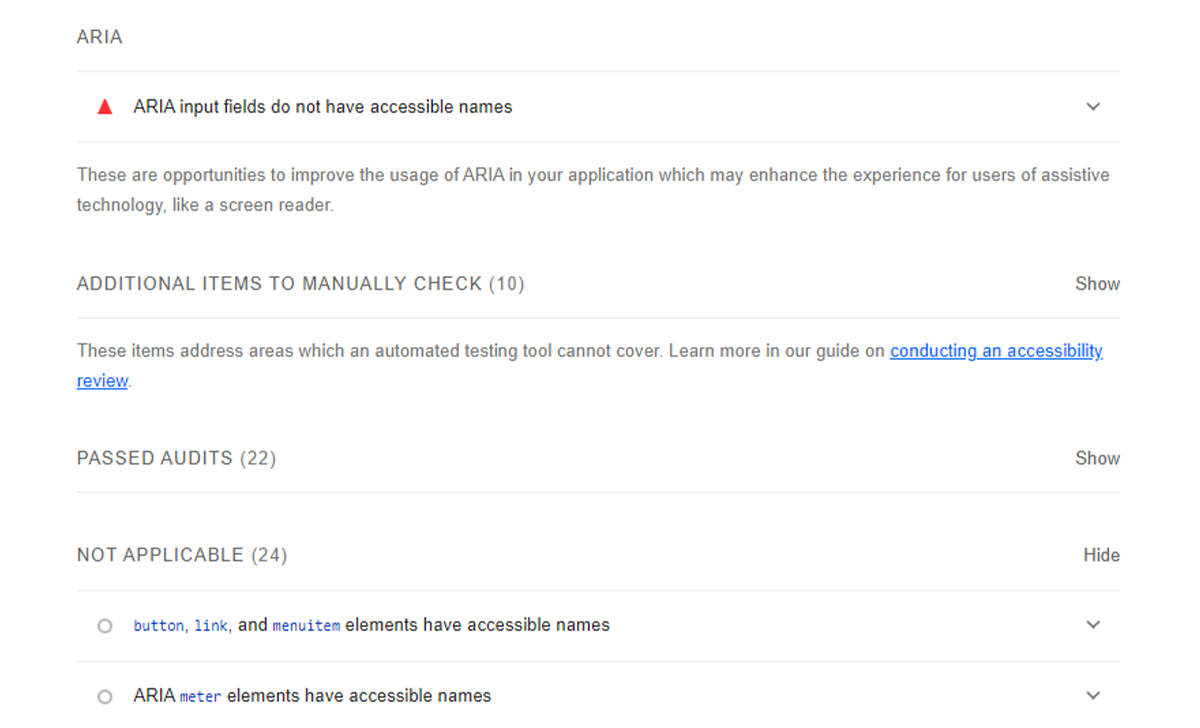
It also reviews site images to see whether alt text is present. When users with poor or no vision use screen readers, they can read the image. Like a performance audit, an accessibility report scores you on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 being the best. As shown in the image above, it also highlights opportunities or suggestions to improve your overall accessibility. Keep reading what is Google Lighthouse score is to optimize your site properly.
Also Read: How To Make A Responsive Website? 8 Practical Tips You Must Follow
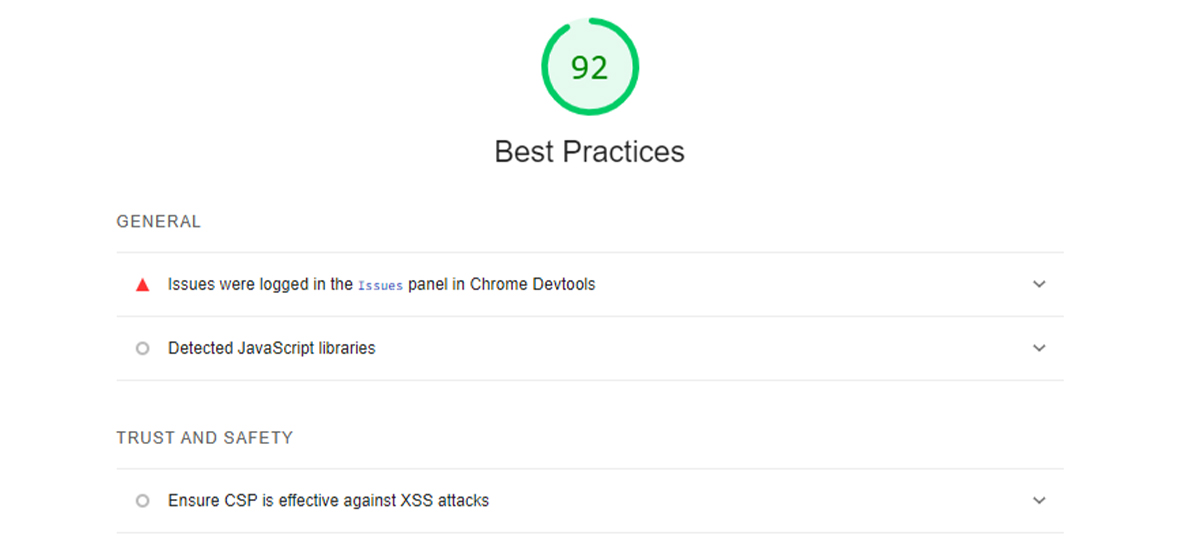
3– Google Lighthouse Best Practices Analysis:
Lighthouse’s best practices audit verifies whether your page is current with the latest web development standards. In addition, it performs a brief audit of generally accepted best practices for web development. Most of these best practices relate to security — using HTTPS, securing outbound & cross-links, keeping up with the latest JavaScript libraries, using APIS, determining the HTML doctype, and displaying images with the correct resolution.
Lighthouse examines whether:
- Page is free from APIs & deprecated frameworks
- The page has valid source maps
- Resources load from secure servers with HTTPS.
- The page has the HTML doctype
- Content Security Policy is effective against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks
- All site images appear with the correct aspect ratio and inappropriate resolution
- Character encoding of the page is set with the meta charset tag
- The page allows users to paste passwords in the password area
- All JavaScript libraries are safe & free from any vulnerabilities.
- The page is free from all browser errors
- The Page is free from problems like insufficient security measures, network request failures, and other browser issues
- The Page creates a good UX by blocking geolocation & notification permission requests on page load.
All these audit factors decide your score out of 100. It highlights specific elements requiring your attention that can improve your score. Keep reading about how does Google Lighthouse work to optimize your site properly.
4– Google Lighthouse SEO Analysis:
As the last graded category, the Lighthouse SEO score assesses how closely your site page adheres to SEO best practices. It runs a test to analyze your webpage for some technical aspects of SEO.
Specifically, it checks whether:
- Page is indexable & Robots.txt is valid
- Whether internal links are crawlable
- The page has a valid hreflang attribute
- Images on a particular page have image alt texts specified
- The page has a viewport meta tag with width or initial-scale set
- Title and meta description tags are set
- Whether your webpage is mobile-friendly
- The page has valid structured data
- Page’s links are introduced with descriptive text
- The page is returning the HTTP 200 (OK) status response code
- The page has a valid “rel=canonical” tag set
- The page content is independent of plugins
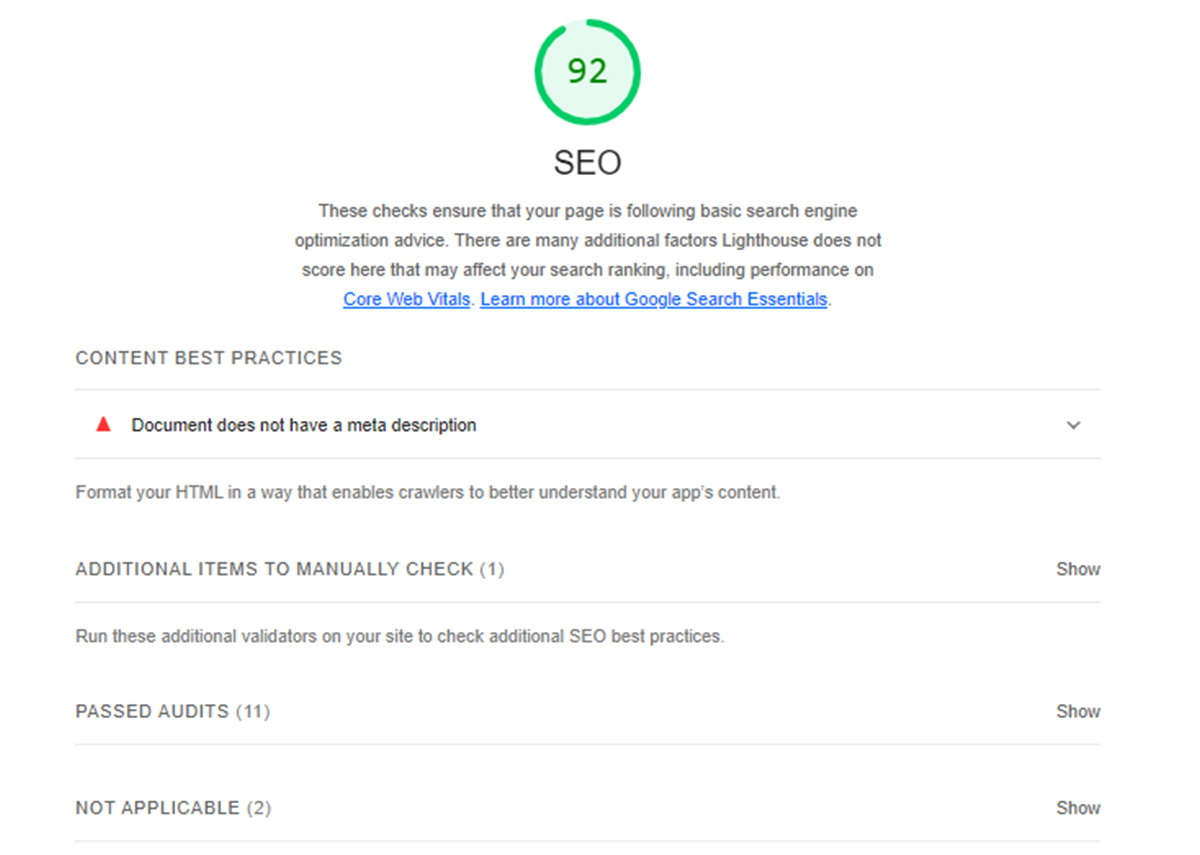
After analyzing these, it assigns a score out of 100 & suggests any SEO issues it detected when running an audit. Lighthouse’s SEO audit report is pretty basic, but it can help you get some quick ideas for your search ranking.
5– Google Lighthouse Progressive Web App
Lighthouse’s final check tests whether your site/web application meets the standards for what Google considers a Progressive Web Application and uses modern web capabilities to provide an optimal user experience. The Progressive Web App Checklist basically describes what makes an app installable and usable by all users, regardless of size or input type. Keep reading what is Google Lighthouse speed test is to optimize your site properly.
See what web.dev mentions about the Progressive Web App (PWA) checklist in their guide:

Image Source: web.dev (Core Progressive Web App checklist)
Difference Between Google Lighthouse And PageSpeed Insights?
Furthermore, while somewhat similar to PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse is different. Lighthouse offers a more holistic picture than page performance (like PageSpeed Insights does).
| PageSpeed Insights | Google Lighthouse |
|
|
Does the Lighthouse Score Affect SEO?
Google Lighthouse is the top recommended tool for measuring Core Web Vitals and other performance metrics. The Google Lighthouse score does not directly impact SEO, but Google looks at real user data to assess UX so that you might get a Lighthouse score of at least 20. However, a slow website in the lab may also be slow for real users. The real-user Core Web Vitals metrics that Google collects are used as a ranking signal, and if your site scores less in Lighthouse, then it definitely performs poorly in front of real users & search engines.
General Google Lighthouse Tips You Can Follow
Like Google PageSpeed Insights, getting your Google Lighthouse score to 100 may take lots of work. Don’t get demotivated if Google Lighthouse mentions dozens of improvements you didn’t consider important. It’s up to you to decide which metrics matter for your website. Here are a few things to remember:
- Since Lighthouse is free & open source, there is a thriving community of contributors & a robust repository to draw from. The issue tracker is an excellent resource for audit metrics and other Lighthouse-related issues.
- If you want thorough guidelines on meeting Google’s standards, follow the Google Chrome Developers blog on how to use Google Lighthouse to improve your website.
- One simple way to limit data requests is to reduce the image’s size where possible. You should inspect your bundle to see if you’re using any third-party code you don’t need, and ensure you compress as much as possible.
- Use Webpack for managing dependencies, which is also essential for optimizing the perceptual speed of projects.
- Note that not all browsers currently support service workers, and ensure your site works for users who don’t have JavaScript enabled. Using the <noscript> tag will allow you to add essential content to be displayed to users even without JavaScript
- Speaking of accessibility, another core principle of (PWA) progressive web design caters to mobile users, which is why Google Lighthouse says to include a meta-viewport in the <head> of your code documents. Doing this will ensure that your app works across various browsers & devices.
To Sum Up:
Page experience is becoming an increasingly crucial factor for Google; it must become equally vital for website owners & developers. Lighthouse provides a somewhat detailed analysis of how Google judges your web pages. Not only is this audit vital to rank well in the search engines, but it also gives you important data into how users experience your website, no matter how they land there. Utilize the reports from Google & learn how to improve your site. Want a professional to audit your website perfectly to improve the user & search engine experience? Contact our SEO experts now.









