Imagine you climb to the top of the SEO mountain…only to realize you’re not the view everyone’s looking at.
Right above you, Google’s shiny answer boxes, maps, and videos are taking all the attention. Yep, those are Google SERP features, and they’re real stars of the search page. If you want clicks, you can’t just rank; you’ve got to stand out.
And here’s the kicker: they can steal clicks from even the #1 ranking. That’s why understanding and optimizing for SERP features isn’t a bonus anymore; it’s an essential SEO strategy.
In this blog, we’ll break down:
- Types of Google SERP features you need to know
- How each one impacts your visibility and traffic
- And what mistakes to avoid when targeting SERP features
Before we dive deep, here’s the simple truth: SERP features are Google’s way of keeping users on the search page, and if you’re not part of them, you’re invisible.
What are SERP Features?
SERP features are specific components that show up on Google’s search engine results page (SERP) that extend beyond the conventional “10 blue links.” These features are unique search results that differentiate themselves from standard organic search results and are designed to enhance the user experience by delivering quick answers and extra information directly on the results pages.
They can take several forms.
Such as Featured Snippet:
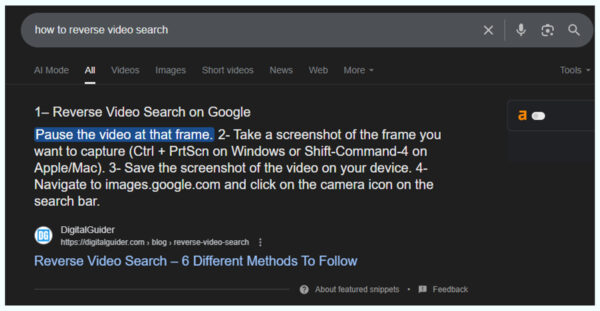
There are other common Google SERP features such as AI Overview, People Also Ask (PAA) boxes, image packs, video carousels, and knowledge panels.
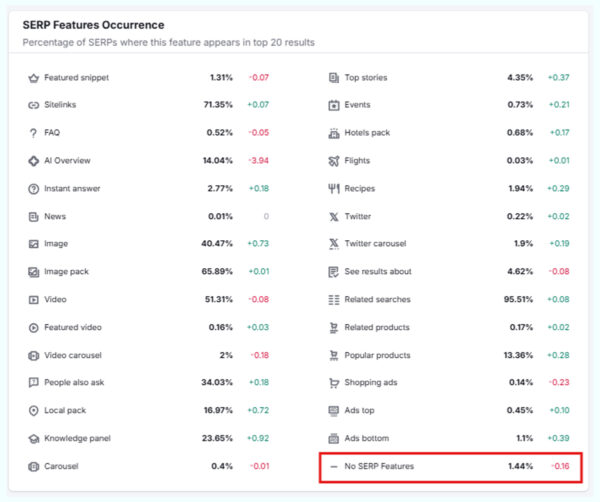
Over the years, Google has persistently introduced new SERP features. You’ll rarely see search results without them.
As per Semrush Sensor data from October 2024, only 1.53% of Google search results are displayed without any SERP elements.
Which is why it is crucial to consider SERP features when selecting keywords and optimizing your content for organic click-through rate (CTR).
Types of Google SERP Features
Understanding these types of SERP features is the first step to optimizing your content and securing prime real estate on Google’s results page.
1. Features Snippet
Feature Snippets are prominent boxes that showcase a particular segment of a webpage. This segment is displayed directly within the search results.
The most prevalent types of Featured Snippets are:
- The Definition Box – a brief text snippet aimed at providing users with a straightforward definition or explanation.
- The Table – a snippet that presents data collected by Google from a webpage and displayed in a table.
- The Ordered List – a snippet that organizes items in a specific sequence. Google often uses Ordered Lists for queries that need a set of steps.
- The Unordered List – a snippet that enumerates items that do not need to follow any specific order
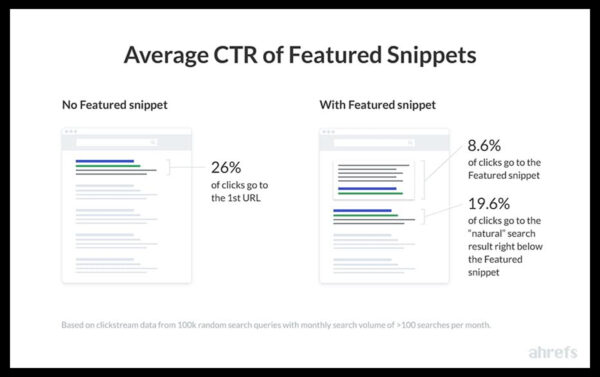
The featured snippet has a significant impact on organic click-through rates. As per Ahrefs, featured snippets receive approximately 8% of all organic clicks
2. Top and Bottom Ads
This one’s simple.
Google’s SERPs usually feature two main ad placements:
- Top of the page – right above the organic results.
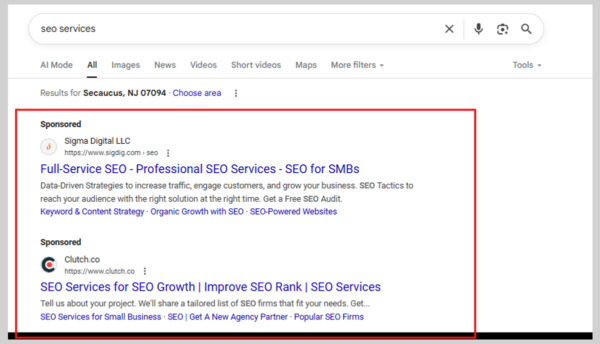
- Bottom of the page – after all organic listings.
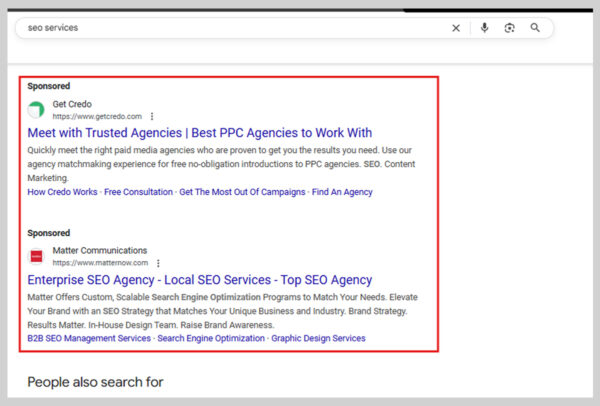
According to WordStream, the average click-through rate (CTR) for Google ads is approximately 3%. That means ads do influence organic CTR, but not nearly as much as Featured snippets do.
3. Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are bits of extra detail that show up alongside a specific search result.
Typically, a Google result consists of three elements: the title, a brief description, and the URL. Rich snippets go beyond that, adding information such as product prices, availability, ratings, or even FAQs, directly in the search results.
These extra details help people quickly decide whether your page is worth clicking. For instance, if you’re browsing for a product, a snippet showing its price and stock status can save you from opening multiple pages.
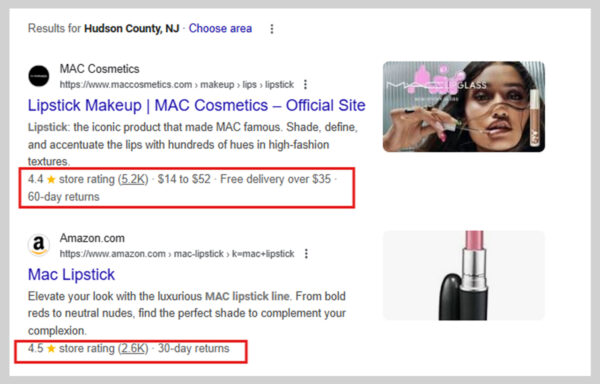
FAQ snippets function similarly, providing users with instant answers without requiring them to leave the results page.
By using structured data on your site, you can greatly improve your chances of earning these enhanced listings.
4. Video Carousels
Video carousels are groups of video results, most often from YouTube, that appear within Google’s search results.
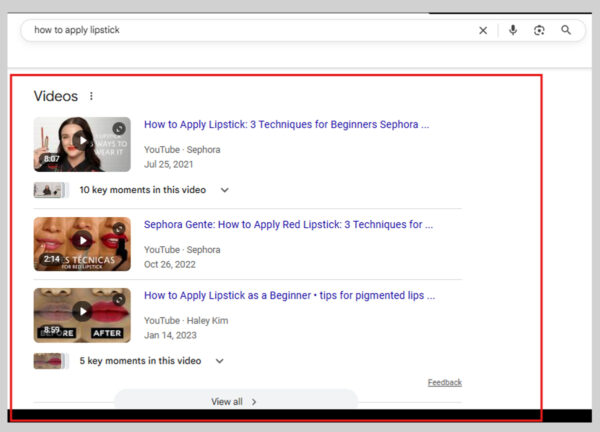
They’re not shown for every query; in fact, research from Semrush suggests that only about 6% of searches trigger them.
When they do appear, they’re hard to miss. Carousels occupy a large section of the results page and often sit right at the top, making the thumbnail images highly clickable.
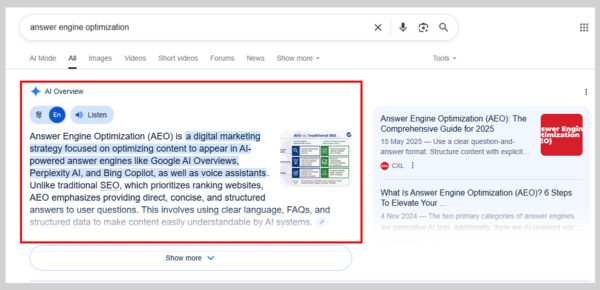
5. Google’s AI Overviews
AI Overviews are brief, machine-generated summaries that appear right at the top of Google’s search results, above every other listing.
They’re pulled from high-ranking pages and can appear for almost any type of query, though they’re most common for informational searches like “what is [topic]”.
Unlike a featured snippet, an AI Overview often provides a more detailed explanation, along with a list of sources shown to the side.
You don’t need a special strategy to show up here. Instead, focus on core SEO practices:
- Make sure your pages are crawlable and indexable
- Publish helpful, high-quality content that answers the searcher’s question
- Show Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T)
- Target the right keywords in your content
- Keep information fresh and accurate
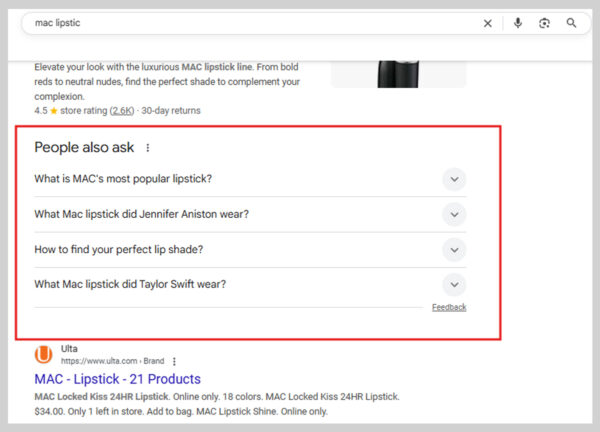
6. People Also Ask Boxes
Data from Advanced Web Ranking shows that PAA boxes appear in about 8.5% of all U.S. search queries.
You’ve probably noticed them; they look like small FAQ sections built right into the search results, each tied to the original query. Clicking on a question reveals its answer and often triggers more related questions to appear.
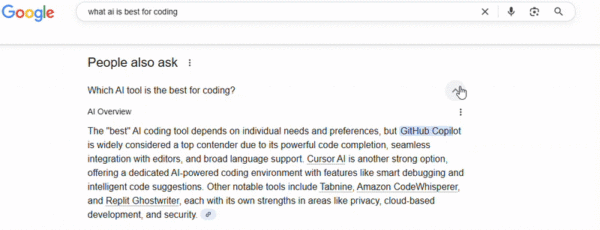
The purpose is simple: Google wants to anticipate what you’ll ask next and give you the answer before you even type it in.
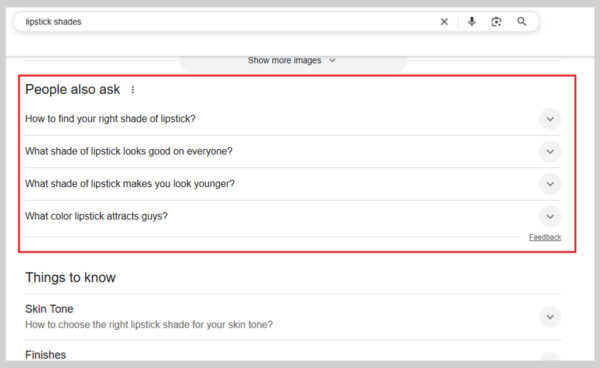
For example, searching for “lipstick shades” brings up a People Also Ask box with follow-up questions you might have in mind. This way, you can get multiple answers in one place without starting a new search.
7. Local Pack
Local Packs, often called “The Map Pack,” are groups of three local business results that appear for searches Google deems location-specific.
Examples include queries like “best coffee shop in Chicago” or “best coffee near me”.
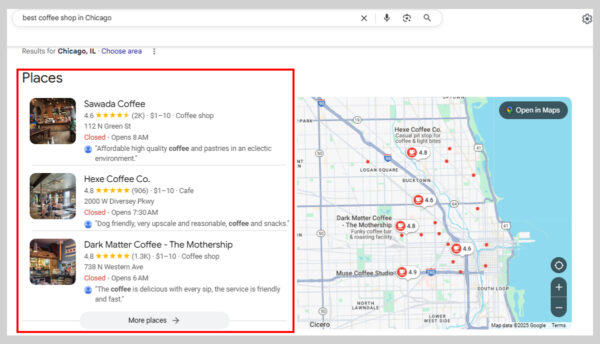
Unlike standard search results, Local Packs run on a slightly different algorithm. While traditional SEO often centers on backlinks, local SEO focuses more on optimizing your Google Business Profile, earning positive reviews, and maintaining accurate NAP (Name, Address, Phone) citations.
For local businesses, or any business with a physical location, appearing in the Local Pack is a big win. These results usually take a prime spot on the page, feature an interactive Google Maps display, and include visual elements that grab attention far more than regular organic listings.
8. Knowledge Panels
A Google Knowledge Panel is an information box that appears on the right side of the search results page, highlighting key facts about a person, place, brand, or other entity.
For example, searching for “Nike” shows the company’s official site and recent news in the main results, while the panel to the right displays details like the founders, CEO, popular product lines, headquarters location, and more.
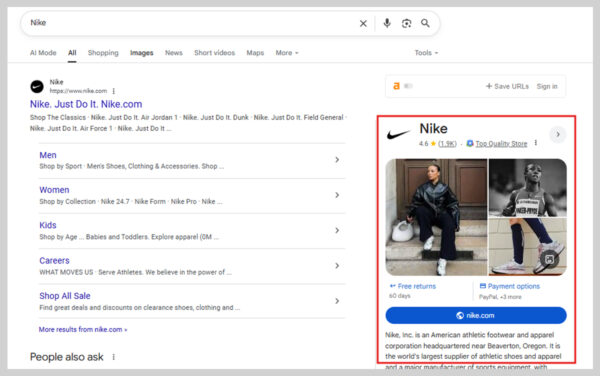
These panels pull data from Google’s Knowledge Graph, a vast database of facts about entities, and typically include descriptions, notable information, and related links.
Appearing in a knowledge panel can boost visibility, drive traffic, and strengthen brand authority. To improve your chances:
- Create a dedicated “About Us” page with accurate details and links only to trusted sources.
- Claim and verify your knowledge panel if one exists.
- Optimize your Google Business Profile.
- Correct inaccurate brand information on external websites.
- Use the organization schema to help Google understand your business.
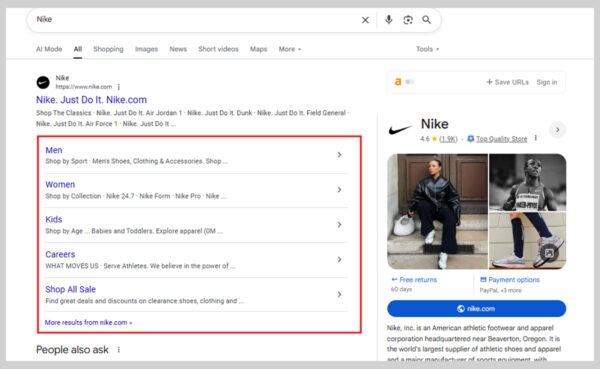
9. Sitelinks
Sitelinks appear in two main forms:
- Links to other pages on a website
- Links to specific sections within a page
In either case, sitelinks show up beneath a standard search result to help users navigate directly to the content they want.
They’re most commonly seen under homepages for branded searches.
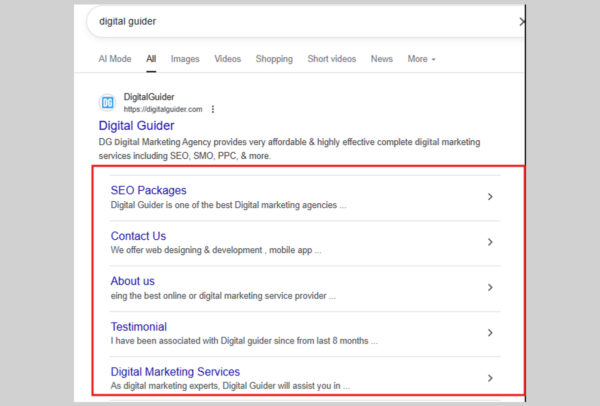
For example, if you search for “Nike”, Google can’t always tell whether you want the homepage, the About page, or the login page. Sitelinks make it easy to jump straight to the right place.
Page-level sitelinks work the same way, letting users see the main sections of a page and click to go directly to that part of the content.
10. Image Packs
An image pack is a collection of images that Google displays directly in the search results, often pulled from Google Images.
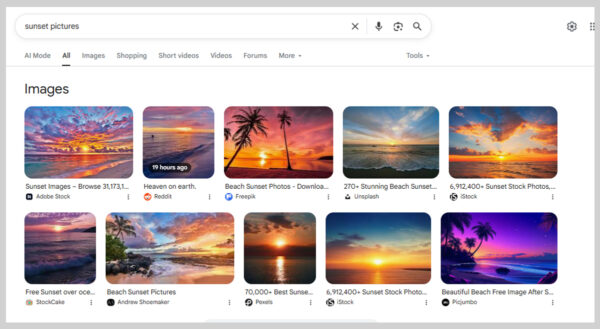
Google decides to show an image pack when it believes users want to see visuals for a query. Some searches make this obvious, like “sunset pictures”. But other times, Google identifies the need based on user behavior, which is why optimizing image SEO matters.
For example, the keyword “office setup” might not seem like it would trigger an image pack, but it does.
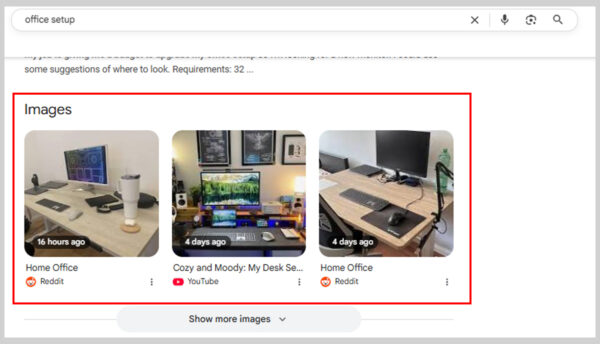
Google likely tested results with and without images and found users engaged more when visuals were included, so it now appears by default.
11. Knowledge Card
Knowledge Cards are boxes that appear at the top of Google’s results for simple, fact-based searches. They pull information from reliable sources and give a direct answer without requiring a click.
They often show up for queries like “distance from Earth to Moon” or “capital of Japan”.
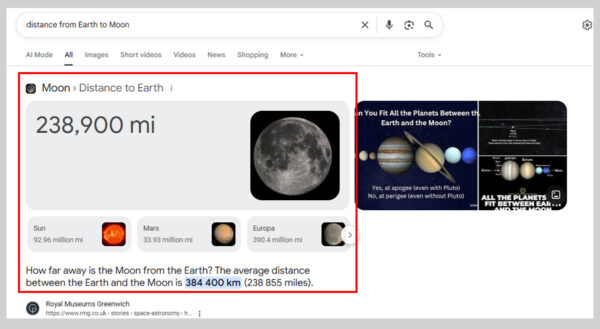
For example, searching for “largest desert in the world” brings up a Knowledge Card with the answer (Antarctic Desert) along with details like size and location.
12. People Also Search For
People Also Search For shows up when you click on a result and then return to the SERP. It suggests related searches based on what others commonly look for.
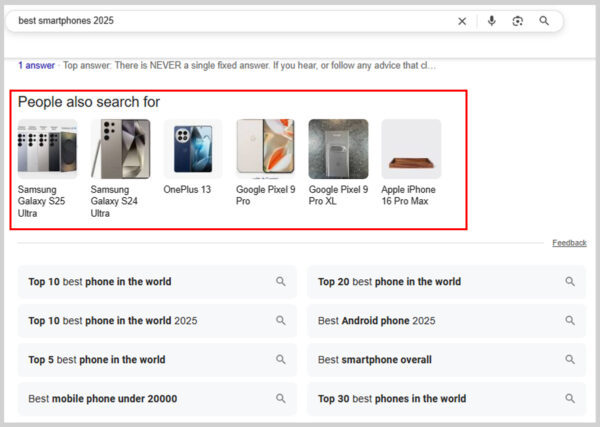
For example, if you search for “best smartphones 2025” and click into a result, PASF might show terms like “OnePlus 13”, “Samsung Galaxy S25”, or “Google Pixel 9 Pro”. This feature helps users refine their search and explore connected topics.
13. Shopping Results(Product Listings)
Shopping results appear when Google detects a product-focused query. These are shown as product listings with images, prices, reviews, and store names.
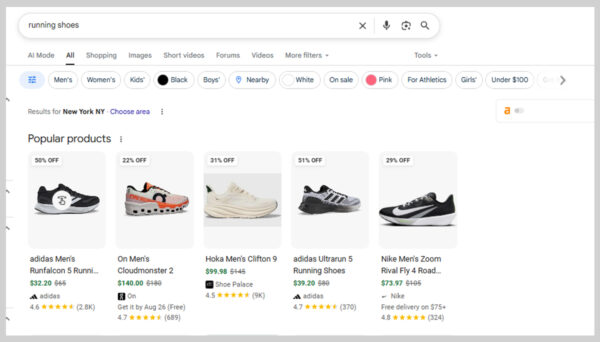
For example, searching “running shoes” often brings up a shopping carousel where you can compare products before clicking through to a store.
14. Top Stories
Top stories highlight recent news articles around a topic. They usually appear near the top of the results page in a carousel format.
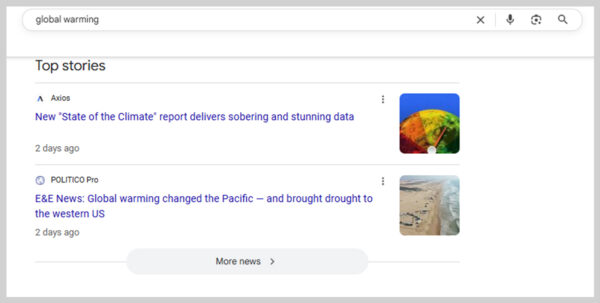
For example, searching “global warming” might bring up the latest headlines from news publishers covering climate change updates.
15. Twitter (X) Carousels
For some trending topics or public figures, Google pulls live tweets (now post on X) into a carousel right in the search results. This makes it easy for users to see the latest updates in real time.
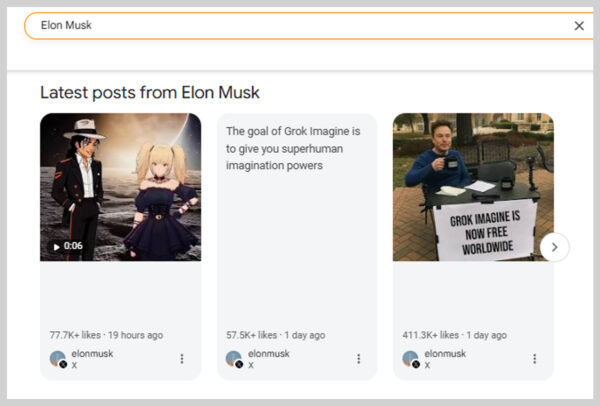
For example, a search for “Elon Musk” may display his recent post and other related trending tweets.
16. Jobs Pack
Google Jobs shows a listing of job openings pulled from different career sites and company listings. It appears in a box where you can filter by location, job title, posting date, and more.
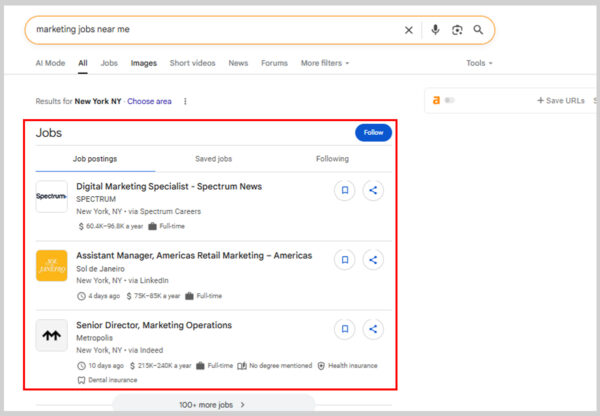
For example, searching “marketing jobs near me” brings up a Jobs Pack with current openings.
17. Events Pack
The events Pack highlights upcoming events related to your search. It displays even names, dates, times, and venues, often with a link to buy tickets.
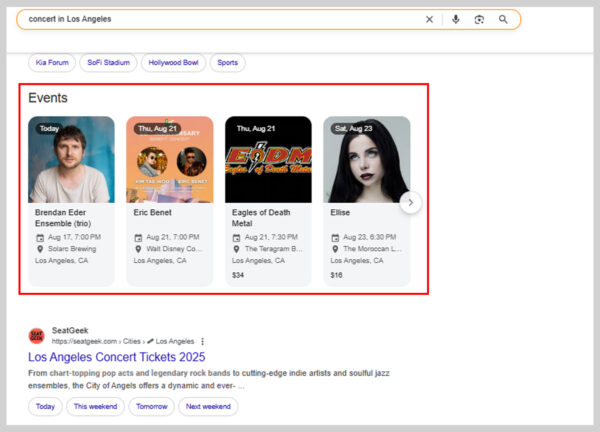
For example, searching “concert in Los Angeles” shows a list of shows happening soon.
18. Flights Pack
For travel-related queries, Google sometimes shows flight options directly in search results. These include airlines, prices, flight times, and booking links.
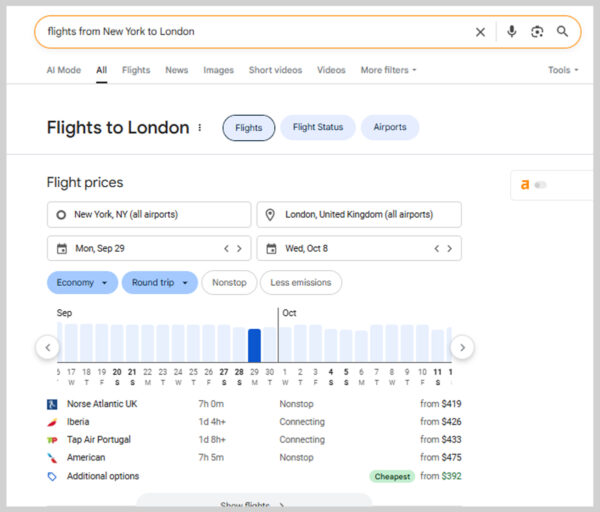
For example, searching “flights from New York to London” brings up a Flights Pack with options you can compare.
Interesting Read – Google Flights: Step-by-Step Guide & Opportunity for Travel Businesses
19. Recipes
For food-related searches, Google often displays recipe cards with images, ratings, prep time, and ingredients.
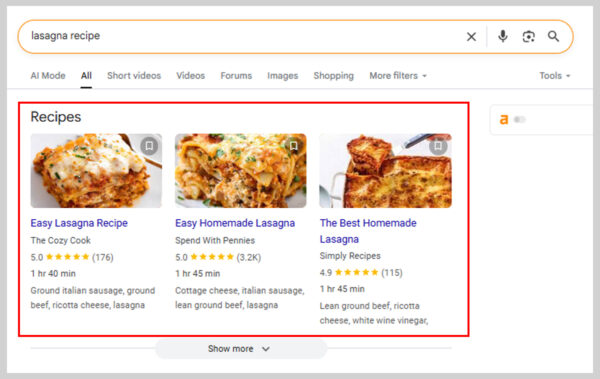
For example, searching “lasagna recipe” brings up a carousel of recipe cards from popular cooking sites.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Targeting SERP Features
Targeting SERP features can bring massive visibility, but many websites make common mistakes that cost them clicks and rankings.
Here are the big ones to avoid:

1. Ignoring Search Intent
Trying to rank for a SERP feature without aligning content to the searcher’s intent rarely works. For example, a blog post won’t win a Local Pack spot if the query is looking for nearby businesses. Always match your content type to the SERP feature you’re aiming for.
2. Skipping Structured Data
Rich snippets, FAQs, reviews, recipes, and products often rely on structured data (schema). Not adding schema markup reduces your chances of appearing in these enhanced listings.
3. Keyword Stuffing
Using the target keyword over and over won’t help you land a Featured Snippet or People Also Ask box. Instead, use natural language, clear formatting (like headings and lists), and answer questions directly.
4. Outdated or Thin Content
SERP features, like AI Overviews, Top Stories, and Knowledge Cards, prioritize fresh, trustworthy information. If your content is outdated, shallow, or copied, Google won’t use it.
5. Overlooking E-E-A-T
Google wants content that shows Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Without these signals, your chances of appearing in high-value SERP features (like Knowledge Panels or AI Overviews) drop.
6. Forgetting About Mobile Optimization
Many SERP features, such as Image Packs, Video Carousels, and Shopping Results, are designed for mobile users. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’ll likely miss out.
TL;DR
Climbing to the top of Google’s results isn’t enough anymore. With Google SERP features stealing the spotlight, visibility depends on how well you adapt.
The key? Create content that answers questions, optimize with structured data, and keep everything fresh, authoritative, and user-focused. Do that, and you won’t just show up in search results; you’ll dominate the SERP and capture attention before competitors even get a chance.
At Digital Guider, we help businesses secure more visibility through SERP features that matter. Let’s turn your rankings into real results.
FAQs
Q1. How do I know which SERP features my site can rank for?
A1. Check your keywords in tools like Semrush or Ahrefs; they’ll show which features show up.
Q2. Can I appear in more than one SERP feature?
A2. Yes, with the right content format and schema, you can.
Q3. How can I use SERP features to gain clicks instead of losing them?
A3. By optimizing for snippets, FAQs, and visuals, you can capture attention directly on the results page and drive qualified traffic.
Q4. How long does it take to show up in a SERP feature?
A4. Anywhere from a few days to a few months, depending on competition.
Q5. Can small businesses compete with big brands here?
A5. Yes, features like Local Pack and PAA reward relevance, not just size.
Q6. How can AI Overviews affect SEO strategy?
A6. AI Overviews surface concise, trusted sources — optimizing for E-E-A-T and structured data boosts your chance of inclusion.
Q7. Is schema markup necessary for every page?
A7. Not always, but it’s key for features like FAQs, products, and recipes.
Q8. Are SERP features important for brand awareness, too?
A8. Yes, even if users don’t click, your brand gets visibility.
Q9. Can I lose a SERP feature once I get it?
A9. Definitely. SERP features aren’t permanent spots. Regularly updating and improving your content helps you keep your position.
Q10. How do SERP features vary by search intent?
A10. Informational queries trigger snippets or videos, while transactional ones show shopping or map packs — intent shapes visibility.







