Canonicalization, authority, author authority, API, KPI — SEO jargon can get overwhelming fast. But if you’re a marketer, business owner, or professional looking to build digital visibility, this SEO glossary is your go-to reference. Designed to strengthen your knowledge and clear away confusion, it will help you approach search marketing with confidence.
In this blog, we’ve compiled SEO terms and definitions in alphabetical order (A–Z) — from the most common concepts to lesser-known abbreviations and acronyms. Whether you’re working on SEO, SEM, or broader digital marketing, this glossary is a handy resource to visit online.
What is an SEO glossary?
An SEO glossary is a collection of definitions for terms specific to the field of search engine optimization (SEO).
It acts as a resource for understanding terminology, acronyms, and abbreviations in SEO, assisting both beginners and seasoned experts in navigating the intricacies of the industry.
An SEO glossary is essential and useful for marketers and business owners, and entrepreneurs because it:
- Provide clarity on key SEO concepts
- Enables better communications within the SEO industry
- Helps in implementing & developing effective SEO strategies
- Supports establishments of E-E-A-T (Experience-Expertise- Authority-Trust) with search engines.
Now, let’s understand and define the SEO glossary of terms from A to Z for easier reference and better comprehension.
This glossary not only covers SEO acronyms, terms, and concepts but also includes key HTTP status codes (like 201,301, 404, 500) that every marketer and business owner should know when dealing with SEO and website performance.
# HTTPS codes
HTTPS codes are a note that is actually given by servers, and are put at the top of the web page. It is a type of message sent by servers to communicate how different requests are processed by the servers.
HTTP codes or response codes are broken down into 5 different classes, namely: 1XX, 2XX, 3XX, 4XX, and 5XX.
Let’s look most important SEO-relevant HTTPS codes with plain-language explanations and their SEO impact.
SEO- Relevant HTTPS Codes | Meaning | SEO impact |
| 200- OK | Request is successful, page loads normally | The status is Ideal. The search engine can crawl & index the page without issue. |
| 301- Moved Permanently | The page has been permanently moved to a new URL | Passes link equity to the new URL. A best practice for redirects. |
| 302– Found (Temporary Redirect) | The page is temporarily at another URL | Does not always pass full link equity. They use short-term moves |
| 304- Not Modified | The content hasn’t changed since the last crawl. | Saves crawl budget, search engines don’t re-download unchanged pages. |
| 307- Temporary Redirect | A temporary redirect that preserves the original request method. | Like 302, signals a transfer expected temporary change, no link equity. |
| 308- Permanent Redirect | A permanent redirect similar to 301, but preserves the request method. | Passes link equity like 301, good for permanent URL change. |
| 403- Forbidden | Server refuses access to the resources | Search engines can’t crawl, thus the content won’t be indexed. |
| 404- Not Found | Page doesn’t exist | Frequent 404s waste crawl budget and hurt user experience. Use 301 if the page has moved. |
| 410- Content deleted | Page has been permanently deleted. | Stronger signal than 404; tells search engines the page should be de-indexed |
| 451- Unavailable for legal reasons | Page blocked due to legal restrictions. | Not indexable; reduces visibility but no penalty. |
| 500- Internal Server Error | The server failed to respond properly | Blocks crawling. Persistent errors harm rankings. |
| 502- Bad Gateway | Invalid response from an upstream server | Search engines can’t access the site. If frequent, it harms SEO. |
| 503- Service Unavailable | Server is temporarily down/for maintenance | Acceptable short-term, but long-term use, risk deindexed. |
📌 For Readers:
- HTTP codes class 1XX are rarely relevant for SEO, and are not included here.
- Also, not all classes and codes benefit SEO; therefore, this table shows the most relevant ones with direct SEO relevance.
150+ SEO Terms You Must Know as a Marketer
A/B Testing
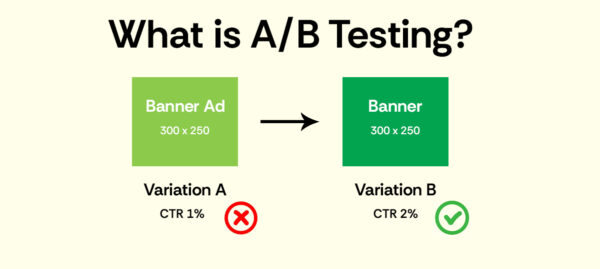
A/B testing is a method of comparing two versions of a webpage or an app against each other to identify which one performs better. It is also known as SEO split testing.
This experimental method involves splitting high-traffic pages into a control group (i.e. unchanged A) and a variant group (i.e. B, with changes), identifying whether improved metrics like organic traffic, CTR, etc.
For example: Testing different meta titles to identify which one leads to a higher CTR (click-through rate).
Above the fold
Above the fold (ATF) refers to the visible area of a web page that can be seen without scrolling. The exact part of the fold varies depending on the device and browser settings.
ATF shapes the first impressions. It is essential for influencing what readers’ eyes see first, helping to catch their attention and encouraging them to stay on the webpage.
Thus, it helps to improve user experience and help to increase revenue.

Absolute URL
An absolute URL contains an entire address from the protocol (HTTP) to the domain address (www.example.com). It provides relevant information for a browser to locate and access the resource regardless of the user’s current location.
The components of an absolute URL are-
- Protocol: It specifies the method for accessing the resource (eg, http://, https:// or ftp://)
- Domain Name: Identifies the specific server or website (e.g. www.example.com)
- Path: Indicates the location of the resource within the website’s file structure (e.g. / image/logo/.png)

Ad Extensions
Ad extensions are additional information about your business, like phone no or a site link that can be added to your ads to make them more informative and appealing to potential customers.
By making ads more noticeable and important, extensions can help get more clicks and improve how well the ads work.
Algorithms
Algorithms are the complex set of rules and processes that search engines like Google use to evaluate and rank web pages in search results.
It helps to analyse various factors to determine which pages are most relevant and authoritative for a given query. Thus, influences a website’s visibility and organic traffic.
Common algorithms that can be considered are Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, RankBrain, etc.
Algorithm Penalty
Algorithm penalty is an automated sanction in a website’s search engine ranking caused by Google’s algorithms. These are detected and penalize violations of its search essentials or quality guidelines.
These penalties can be triggered by keyword stuffing, spammy backlinks, or low-quality content.
Ambiguous Intent
Ambiguous intent refers to the users’ search queries that are unclear and make it difficult for systems like search engines or virtual assistants to understand the true purpose of the input.
For example, a single word query like “appe”- it is unclear whether the users want to search for the fruit or the brand.
ALT Attribute (Alt Text)
Alt attribute, also known as “alt text” or “alt description”, is a text alternative (alt= alternative) to images, to describe a graphical image on a website. It is usually a few characters, but with great significance. ALT text not only ensures accessibility, but it is also an important SEO factor.
Example: <img src= “coffee.png” alt= “fresh coffee beans”>
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
Google launched an open-source project to help publishers create webpages, optimize content for all devices & operate at optimal speed. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) can help with SEO in several ways, like better UX, providing higher ranking & visibility, getting more traffic, higher click-through rates, faster loading, better page speed & lower bounce rates.

Anchor Text
Anchor text is a visible, clickable text within a hyperlink that users see, and it helps them navigate to another web page or source. It is also known as a link label or link text. The anchor text is often blue in color and underlined in modern browsers.
It plays a crucial role in SEO strategy, influencing link building, internal linking, and user navigation.
In the image below, “search engines” is the anchor text.
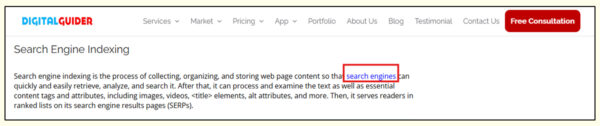
Authority
Authority refers to a website’s credibility and trustworthiness in the eyes of a search engine like Google. It signals to potential to rank well for specific queries. The authority is measured based on site links, relevance, quantity, quality, and prominence.
It primarily focuses on the 3 core elements, i.e. domain authority, page authority, and topical authority.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. It serves as an umbrella term that encompasses technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP).
AI powers a wide range of everyday applications—from recommendation engines suggesting movies or products, to chatbots providing real-time customer support, to systems capable of reasoning and decision-making. In essence, AI is the driving force behind many of the smart tools and services we now rely on daily.
Advanced Search Operator
Advanced search operators are special commands, characters, or symbols that are used in the search engine’s query box to filter and refine results, making them more precise. These operators help filter, narrow down, or expand searches beyond basic keywords.
Example:
Site: limits results to a specific domain (e.g., site: xyz.example).
intitle: finds pages with specific words in the title (e.g., intitle: SEO guide).
Filetype: searches for specific file formats (e.g., filetype: pdf marketing strategy).
These are often used by marketers, researchers, and SEO experts to use these operators to uncover insights, analyze competitors and discover information efficiently.
AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)
Answer engine optimization is the process of optimizing content so it is easily found and featured by AI-driven answer engines like Google Assistant, voice assistance (like Alexa), and even chatbots like ChatGPT and Gemini.
It is very important, as users shift towards voice search and chatbots, that they prioritize quick, precise responses over long result lists.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites that lead to your website. These are only links to your website made on another website (referred domain). They are also referred to as incoming or inbound linkages. Backlinks are a solid vote of confidence from other websites. It means that they would rate your content at a high level.

Backlinks are essential to SEO since they encourage search engines to see that the site is valuable and relevant. Search engines will rank your website higher the more backlinks it has. This is so that Google will recognize that the website is well-known and reliable if reliable websites are linked.
Blackhat SEO
Blackhat SEO refers to the unethical practice used to increase a site or page’s rank in search engines by violating the guidelines and often misrepresenting the content or relevance of the site. Examples of Black Hat SEO are keyword stuffing, hidden text, link farming, and private blog networks (PBNs).
While black hat seo impacts SEO by giving a short-term ranking hike, it almost results in penalties, loss of ranking, or even complete removal from search engine indexes.
Branded keyword
Branded keywords are the search terms or search keywords that use a specific brand name, product name, or any variation of it, which indicates the user’s intent to search for a particular brand’s website or products.
Example: “newly launched Nike Shoes for women”, “latest model of Apple iPhone”, etc.
Such keywords have high conversion potential due to brand familiarity, credibility and ensuring the brand’s visibility in search results for those searching for it.
Breadcrumb
A breadcrumb is a small text path located at the top of the page, which helps us navigate and indicate to the user where exactly they are on the site. In the images below, the hierarchy-based breadcrumb navigation is Home>Video SEO>Vlog Video Production Services.

All these steps are clickable are return to the homepage. Breadcrumbs improve user experience, reduce bounce rate, and provide structured data for search engines, often appearing in SERPs to enhance click-through rates.
Broken links
A broken link is a hyperlink that points to a page or resource that does not exist. These linked pages were often deleted or moved without a redirection setup. To redirect broken links for SEO, some recommend using a 301 redirect. A 301 redirect lets a search engine know that a page has moved to another location. This passes the SEO properties of the old page to the new page.
Broken link building is a tactic that involves finding a dead page and asking linkers to swap the links to a working page on a site. This is also known as Dead Link Building.
Barnacle SEO
Barnacle SEO is a digital marketing practice where you attach your website to another website which ranks highly for your target keywords. It is also known as parasite SEO. It doesn’t rely on your own website; instead, stick to the one that performs well in Google.
Therefore, it helps improve visibility, drive referral traffic, and boost brand authority for competitive keywords where your site may not rank easily.
Brand Mentions
In today’s evolving SEO landscape, brand mentions have emerged as a significant factor influencing search engine rankings and overall digital reputation. A brand mention is a citation or implied link on another website that informs readers about a website without linking. Brand mentions can help with SEO because Google treats them as suggested links.
These links or unlinked mentions provide search engines with contextual insights into a brand’s authority and relevance in its industry. Unlinked brand mentions are online mentions of a brand that do not link back to the brand’s website. Once identified, users can contact the website or journalist and request that the mention include a backlink to the brand’s website.
Brand Authority
Brand Authority refers to the trust and credibility a brand earns within its niche, positioning it as an industry expert. Factors like high-quality content, strong media presence, customer engagement, and reviews help build and demonstrate brand authority.
In SEO, strong brand authority improves search visibility, attracts natural backlinks, and increases click-through rates as users are more likely to trust and choose authoritative brands in search results.
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate refers to the site visitors who leave your site after viewing the webpage without interacting further. A high bounce rate results in poor website design, low-quality or irrelevant content, and slow loading speed.
They are often believed to be a negative ranking factor and considered noisy and spammy links for ranking factors by several Google representatives.
BoFu
BOFU, bottom of the funnel, which directly indicates conversions. It represents the last stage of a customer’s journey. The highly qualified leads are ready to be purchased and await a final nudge. The BoFu SEO strategies focus on using high-intent keywords, using compelling landing pages for conversion and by providing content like case studies, testimonials, etc.
Canonical Tag
A canonical tag is an HTML link also known as “rel canonical”, which is a method used to tell search engines that a particular URL, called the canonical URL, is the master version of a page when multiple pages contain the same or similar content.
It helps to identify duplicate content, choose a master URL, and implement the tag; they are very important in SEO by preventing duplicate content issues, consolidating link equity, and improving crawling efficiency.
Commercial keyword
Commercial keywords are the words and phrases searched or researched by the researcher about a particular service or product. This points out the user’s intent to buy or use a product or service. They often use the cue terms like “reviews”, “price”, “buy”, “discounts” or the name of a specific product, etc.
Canonical URL
The canonical URL is the top address for a user to find information, & Google considers it the most representative page from a group of duplicate pages. Sometimes, you might have a situation where the same content page can be accessed at multiple addresses.
Marking the canonical URL helps search engines understand which content address is the best. Most of the time, this is the source URL. The canonical tag goes in the page’s <head> section and looks like this: <link rel=”canonical” ref=”https://www.example.com”>. Below, you can see the canonical URL example on the inspect page.
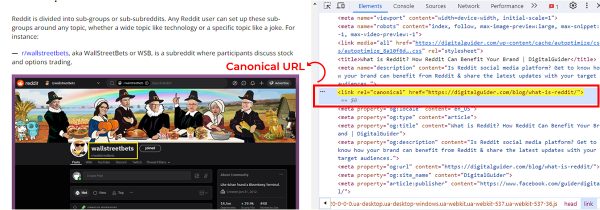
Cache
A cache is a stored version of a web page that shows the search engine last crawled and indexed, as it saves a copy of the page’s HTML content in its database. Cached pages make sure that it is accessible to users. Some search engines that offer cached versions of web pages include Google Search, Bing, Yandex Search, and Baidu. To check whether your page caches, type “cache” before the web page’s URL. i.e., “cache:https://examplesite.com.”
Cloaking
In search engine optimization, cloaking is the practice of displaying different versions of a website to users and search engines. It’s a deceptive tactic that aims to “cheat” the search engine’s algorithm. For example, a website might optimize a page with some text or keywords for search engines while showing prohibited or unrelated images to the users.
Core Web Vitals
A set of metrics that measure the page’s performance related to user experience. Core Web Vitals were introduced alongside the Page Experience update as the main signals that indicate a good user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – loading performance.
- First Input Delay (FID) – interactivity.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – visual stability.
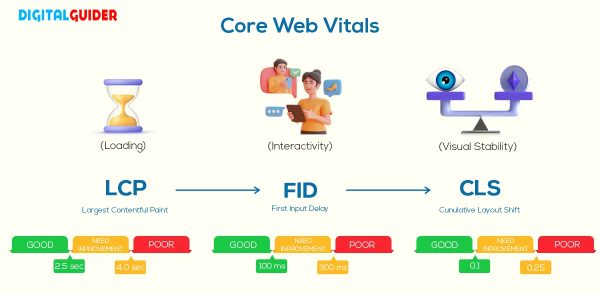
Google did confirm Core Web Vitals as a ranking factor, but said that relevance and other factors may be more important. Google Lighthouse is the top recommended tool for measuring Core Web Vitals and other performance metrics. A slow website in Google Algo Lab may also be slow for real users. The real-user Core Web Vitals metrics that Google collects are used as a ranking signal, and if your website scores less in Lighthouse, it performs poorly in front of real users & search engines.
Content Pillar
A content pillar is the cornerstone of a strategic content marketing approach, representing comprehensive and authoritative content as the central hub for a specific topic. Content pillars are the main topics businesses publish on their websites, social media, and other platforms. It goes beyond a single blog post, encompassing various aspects and subtopics of the main theme.
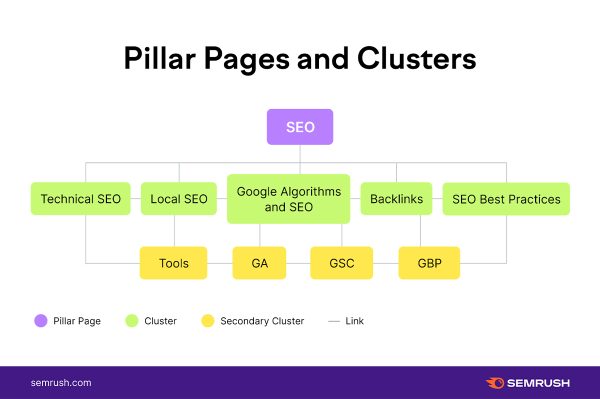
Image source: Semrush
This robust content piece is then strategically interlinked with supporting articles, creating a topical cluster that reinforces the website’s authority.
Co-citation
Moz founder Rand Fishkin first used the co-citation term in an SEO context. In SEO, co-citation is when two different sources mention a website but do not necessarily link to it. For example, if a Search Engine Journal is mentioned on many websites, even if it isn’t linked, Google will consider this co-citation. It can impact search engine perception of relatedness.
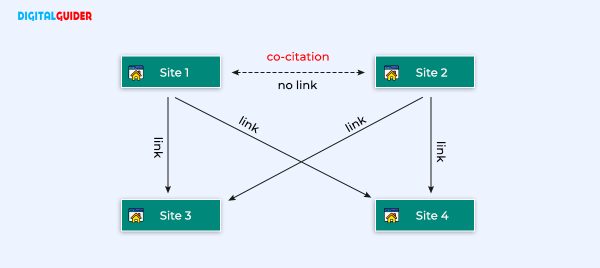
Co-citation is a measure of the semantic relatedness between two documents. It’s based on how often other documents mention them together.
CTR (Click-Through Rate)
Click-through rate is a marketing metric that calculates the percentage of people who see an online ad and click on it. The formula used for the calculation of CTR is
| (Clicks ÷ Impression) × 100 |
For example, your blog post appeared 1000 times in Google search results (simply known as impressions), and out of which 300 people clicked on your blog link, so your CTR percentage calculated will be 30. Thus, the higher the CTR, the more relevant and appealing the ad or link is to users.
Conversion Rate
Conversion rate refers to the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (purchase, signup, form fill). Shows how SEO traffic converts into business results. The formula used for the calculation conversion rate is
| (Conversions ÷ Total Visitors) × 100 |
For example, if 100 people visit your online store and 5 of them make a purchase, your conversion rate is 5%. It’s one of the clearest ways to see if your SEO efforts are turning into business results.
CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization)
Conversion rate optimization is the process of improving your percentage of visitors who complete a desired action. SEO brings people to your website, but CRO makes sure they don’t just visit and leave. It is a way of turning traffic into revenue.
For instance, changing the color of a “Buy Now” button or simplifying a checkout page can boost conversions.
CMS (Content Management System)
A CMS is the platform used to manage a website’s content. WordPress is the most common one, but others like Wix or Joomla also exist. With a CMS, you don’t need coding knowledge to publish a blog or update product pages—it makes running a site much easier.
Crawler
A crawler (or spider) is the program search engines use to scan websites. Googlebot is the most well-known example. It browses through links, collects information, and stores it in the search engine’s index, which later decides what shows up in search results.
Crawl Budget
A crawl budget is defined as the maximum number of pages Googlebot crawls on a website within a specific timeframe. Search engines can only crawl a certain number of your site’s pages at a time.
If a website has thousands of pages, but a lot of them are duplicates or irrelevant, Google may waste time on the wrong ones. That’s why maintaining a clean structure and optimizing key pages is crucial.
Crawl Error
A crawl error occurs when a search engine, like Googlebot, encounters a problem or fails to access or index a page on your website, which impacts your ability to rank in SERPs, decreasing your organic traffic and overall SEO performance.
You can use tools like Google Search Console (GSC) for reviewing reports, or use other SEO tools to check crawl errors by providing technical site audits.
Click Depth
Click depth refers to the number of clicks it takes to reach a page from the homepage. For instance, if a product page is three clicks away (Home → Category → Subcategory → Product), its click depth is 3. Pages buried too deep are harder for both users and search engines to find.
Deep Linking
Deep links are essential as they allow your audience to access specific content within a website instead of just landing on the homepage or about us. This SEO strategy improves internal linking and user navigation. Users are taken directly to the appropriate page or screen by clicking on a deep link, saving them time and effort.
This can help content rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs) and make it easier for users to navigate the website. You can link to a landing page hoping to get new subscribers or link to other content on your site that’s relevant to the topic visitors are already on. Here are some benefits of deep linking: increased user engagement, improved conversion rates, & enhanced marketing and advertising.
Disavow Links
Disavow in SEO means to discard harmful links pointing to your site. If you believe low-quality links damage your site’s ranking, you do not control it. By disavowing your toxic backlinks, you can request that Google eliminate artificial, spammy, or low-quality links when evaluating your website.

Building and earning backlinks to your site can be a great way to boost your SEO and increase your site’s credibility & traffic. However, irrelevant backlinks can also be just as damaging to your site. You may get spammy links from competitors trying to take you down, or they may get those links using black hat techniques.
Disavowing can be helpful when you want to remove the impact of a particular link that is bringing down your website in search engine rankings. It allows you to manage your website’s backlink profile and optimize it.
Domain Authority
Domain authority, commonly called DA, is defined as a search engine ranking score developed by Moz that helps predict how likely a page rank on SERP (Search Engine Results Page). It describes its relevance for a specific subject area or industry.
The DA is marked on a scale of 1-100, where 100 indicates the highest chance of ranking. Any website between the scores of 50-60 is considered a good ranking, and above 60 is considered an excellent ranking.
📌Takeaway
DA is crucial but not a Google ranking factor, with no actual bearing on SERPs. As quoted by John Muller expert from Google, “Google doesn’t use Domain Authority *at all* when it comes to Search crawling, indexing, or ranking. This is pretty clear on their site.”
Domain Name
A domain or domain name is the human-friendly address of a website (www.example.com), which is an easy-to-remember address used to access websites. Domains are secured via registrars and interact with the Domain Name System (DNS) to convert the name into the exact IP address of the server that houses the website’s files.
The domain name is structured with
- Top-level domains (TLDs): they’re the last part domain name, like .com, .org, etc
- Second-level domains (SLDs): It’s the unique name of the site, like example in example.com
- Subdomains: the part of the domain name which is added to the left, mai. Google, or www.google.com, organises the content and services. Within the large domain.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to significant or identical text that exists on multiple web addresses, whether within a single site or spread across various sites. It doesn’t allow getting a penalty over it, but confuses Google in understanding which version of the content is the authoritative source.
Common causes that lead to content duplication include multiple URLs for the same page (e.g., with/without “www” or HTTP/HTTPS) or content that’s been copied and republished on another site.
Do-follow Link
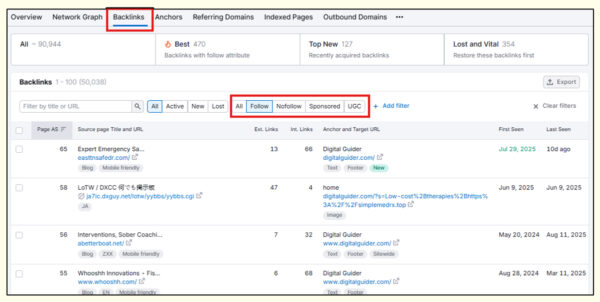
A dofollow link or follow link is a typical, default type of backlink that transfers search engine authority and ranking strength from one site to another. It is a regular hyperlink, with no special attributes like “nofollow”, “ugc” or “sponsored”.
You can find your do-follow links from Semrush as shown in the image above. It helps to boost the linked page’s authority and search engine rankings.
De-indexing
Deindexing is the practice of removing a webpage or website and making it invisible in search results. The practice of de-indexing can occur for multiple reasons, ranging from a technical error to a manual action or a broader trust issue. Also, you yourself can deindex your content by using the nonindex tag or the X-robot tag.
E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T stands for experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. It is a framework used by Google to evaluate the quality and credibility of content on a website. It is used to determine how to rank content in its search results, prioritizing pages that determine qualities.
External Link
An external link is a hyperlink that directs users from your website to a different domain. Also known as an outbound link, it aids users in finding additional resources beyond your site. From an SEO standpoint, external links can add context, boost credibility, and indicate relevance when they connect to reliable sources.
Enterprise SEO
Enterprise SEO refers to the large-scale search engine optimization techniques designed for organizations with large websites, numerous product lines, or a worldwide presence. It emphasizes managing thousands of pages, optimizing workflows across departments, maintaining technical integrity, and ensuring uniform branding in search results.
Entity-Based SEO
Entity-based SEO is a strategy that transcends keywords and concentrates on individuals, locations, brands, or concepts identified as entities by search engines. By establishing authority around these entities and linking them through structured data, the content aligns more closely with how contemporary search engines interpret and deliver information.
Engagement Metrics
Engagement metrics assess how users interact with your website. These encompass the duration spent on a page, bounce rate, number of pages viewed, and click-through rates. Although they are not direct ranking elements, they offer insights into content quality, user experience, and possible areas for SEO enhancement.
Entry Page
An entry page is the initial page a visitor arrives at when they access your website via search engines, social media, or external links. Unlike the homepage, entry pages can be any optimized page, such as a blog post or service page, that attracts organic traffic and directs users further into the site.
Exact Match Domain (EMD)
An exact match domain is a URL that corresponds precisely to a target keyword, such as bestshoes.com. While EMDs previously enjoyed significant ranking advantages, search engines now prioritize content quality and relevance more heavily. Nevertheless, a well-branded EMD can still enhance user trust and click-through rates.
Focus Keyphrase
A focus keyphrase is the primary keyword or phrase around which a particular piece of content is tailored. It serves as a guide for crafting titles, headings, meta descriptions, and on-page content. Selecting the appropriate keyphrase aids search engines in comprehending the subject matter and enhances the likelihood of ranking for pertinent searches.
FAQ Block
An FAQ block is a segment of a webpage that addresses frequently asked questions from users in an organized manner. When enhanced with schema markup, FAQ blocks can show up directly in search results, boosting visibility and delivering quick responses that promote higher click-through rates.
Featured Snippet
A featured snippet is a prominent result at the top of Google’s search results that gives a brief answer to a query. Securing a featured snippet necessitates clear, well-organized content that directly responds to user inquiries, often formatted as lists, tables, or concise paragraphs.
A footer link is a hyperlink located in the lower section of a webpage. While frequently utilized for navigation or legal details, an overabundance of irrelevant footer links can dilute SEO effectiveness. However, well-planned footer links can enhance site organization and user accessibility.
Faceted navigation enables users to filter and organize products or content based on characteristics such as price, size, or category. While beneficial for user experience, it can lead to duplicate content or crawling challenges if not handled appropriately with SEO best practices like canonical tags or noindex directives.
Findability
Findability refers to the ease with which users can discover your website or specific content through search engines or on-site navigation. Strong findability hinges on SEO techniques such as keyword optimization, internal linking, and a clear site structure, ensuring that both users and crawlers can quickly access the relevant content.
Google Search Console (GSC)
Google Search Console is intended to display how your website shows up in Google search results. It notifies you of indexing problems, highlights the keywords that generate clicks, and provides insights on page experience metrics such as Core Web Vitals. Tasks like submitting sitemaps, checking URLs, and tracking coverage errors are common activities performed within GSC.
Google Algorithm
The Google algorithm is the system that determines the order of pages in search results. It evaluates hundreds of factors, including relevance, authority, and user experience. Updates like Panda, Penguin, and the Helpful Content update have transformed the way websites are ranked, favouring valuable content while penalizing deceptive practices.
Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business)
Google Business Profile is a listing tool that boosts a company’s visibility in local search and on Google Maps. An optimized profile shows key details like your name, address, phone number, reviews, and photos. Active management, like adding updates, responding to reviews, and keeping details accurate and can directly improve local rankings.
Google Penalty
A Google penalty occurs when a website is flagged for violating search guidelines. This may result from a manual review or be triggered by an algorithm update. The consequences can be severe, leading to decreased rankings or removal of pages from search results. Addressing a penalty typically involves cleaning up suspicious links, enhancing low-quality content, and adhering to Google’s standards.
Googlebot
Googlebot is the crawler that explores the internet and adds pages to Google’s index. Its operations are affected by crawl budget, robots.txt configurations, and internal linking strategies. If critical pages are blocked or not linked appropriately, they may not show up in search results at all.
Google Knowledge Panel
A Knowledge Panel is the information box that occasionally appears on the right side of Google search results. It can showcase details about an individual, a business, or an organization, gathering information from reliable sources and structured data. Having a Knowledge Panel enhances trustworthiness and brand visibility.
Guest Posting
Guest posting refers to the process of composing and publishing an article on someone else’s website. When executed properly, it can yield high-quality backlinks, referral traffic, and increased brand visibility. However, engaging in low-quality or irrelevant guest posting can be detrimental and may lead to penalties, so choosing the right sites is crucial.
Geo-tagging
In SEO, geotagging is like adding geographical metadata, such as latitude & longitude coordinates and place names, within website content or media files to enhance local search relevance. This can include web pages, images, videos, or social media posts. Geotagging can help improve the visibility of online content in location-based searches. For example, if you’re running a French restaurant in New York and people search for “French restaurants nearby,” you can improve your chances of being shown to them in the top results if you’ve geotagged your content.
Google Trends
Google Trends is a tool that illustrates how the interest in a particular search term fluctuates over time. It enables comparisons among various keywords and reveals seasonal trends or emerging topics. Content creators frequently utilize it to identify opportunities and strategically time their content launches.
Google Tag Manager (GTM)
Google Tag Manager is a tool that simplifies the management of tracking codes without requiring direct modifications to the website’s code. With GTM, marketers can establish event tracking for clicks, downloads, or form submissions. While it does not influence rankings, it enhances the precision of performance data that informs SEO strategies.
Head Terms
A head term, also known as a head keyword, is a word or phrase that is the focus of a search. Head terms are usually one or two words long and are the most specific and relevant keywords in a search query. Head terms are very competitive regarding ranking, and they are the opposite of long-tail keywords.
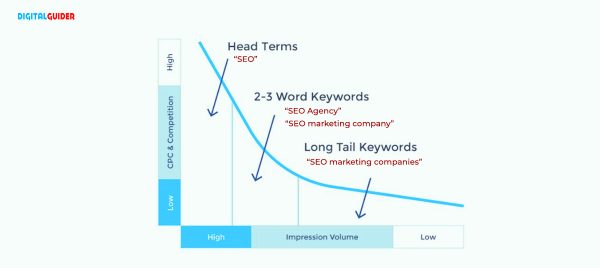
It’s crucial to boost organic traffic while maintaining your website’s competitiveness. Because they encompass a large topic or represent a well-known idea, they may be well-liked search queries with a high search volume.
Header Tags (H1- H6)
Header tags are the HTML tags used to format the headings and subheadings of a webpage. It is also known as heading tags. There are header tags H1-H6, respectively. They allow visitors and search engines to understand the structure of the content, its hierarchy, and the relationship of the headings and subheadings. Therefore, it’s important for SEO and UX purposes.
Hidden Text
Hidden text in SEO refers to the text that is invisible to users or readers but can be seen by search engines. It is considered a spam technique used from the beginning of search engines to include an extra keyword inappropriately, which is manipulative and can be penalized by search engines. The hidden text includes text in the same color as the background, positioned off-screen, or hidden by CSS techniques.
Image source: loganix
Homepage SEO
Homepage refers to the process of optimizing your homepage or landing page for Google or any other search engine, and to get ranked. A homepage can rank your brand keyword if it follows the standard SEO principles, an effective homepage UX, and content optimization strategies.
The optimization of a site’s main page, including title tags, meta description, internal links, and brand positioning. Since the homepage often has the highest authority, it’s critical for the overall SEO strategy.
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a secure version of HTTP. HTTPS uses an encryption protocol called TLS (Transport Layer Security) to increase security while transferring sensitive data, like logging into a bank account, email service, or any other service.
Heatmaps
A heatmap or heat map is a two-dimensional representation of data in which various values are represented in colors. It is an immediate visual summary of information across two axes, allowing users to grasp important and useful information instantly.
For example, a heat map showing the pollution in different cities (range of values) grouped by months using varied shades of red, yellow and and green. The months may be mapped on the y-axis and the pollution ranges on the x-axis.
📌Interesting Read:How Color Psychology is Used in Marketing (With Real Examples)
Image source: userpilot
Inbound Link
An inbound link is a link from another website to your website. It is also known as backlinks, inlinks or incoming links. Inbound is generally used by the person receiving the link. These links are crucial for SEO, as they show the credibility and authority to search engines like Google.
There are 2 types of inbound links: high-quality and low-quality. High-quality inbound links come from good and relevant websites, enhancing the performance. Whereas low-quality inbound links or artificial links can spam your website, thus harming your site’s performance.
Internal Link
Internal links are any hyperlinks from one page of your website to another page of your website, such as an image, or document or content. These links tend to establish a website’s hierarchy and are used by your users and search engines to crawl, navigate and discover new pages on your website.
Internal links are helpful in various ways,
- Navigate the user from one page of the website to another
- Pass on the link equity
- It also helps influence the sitelinks on SERPs.
Informational keyword
Informational keywords are search terms or words typed into the search bar by a user when they want to find information, a solution or guidance on a specific topic. These keywords are often in an interrogative (query form), and generally start with words like “what”, “why”, “how”, etc. and include cue terms like “guide”, “tips”, “benefits” or “features”.
Index Bloat
Index bloat is a situation in which a search engine like Google indexes a number of low-quality or irrelevant pages on a site. This situation happens with slipping of unless pages by the search engines while indexing the useful pages. These result from technical issues like soft 404, paginated pages, low-quality pages, duplicate pages, etc.
Impression
Impression simply refers to the number of times a user sees a link, ad, video, or image on a SERP, whether the user clicks on it or even scrolls to it. It is used to measure your website’s visibility and potential reach.
Keyword
Keywords, aka “keyphrases,” are words or phrases that represent a brand, its products, or services. They help search engines & users understand what a web page is about. For example, if you want to buy a new jacket, you might type something like “women’s leather jacket” into Google. Even though that phrase consists of more than one word, it’s still a keyword. Your keyword should be relevant, have a high search volume, and align with user intent, & target lower competition.
Recommended Blog: How To Do Keyword Research for SEO- 10 Proven Ways
Keyword Cannibalization (H3)
Keyword Cannibalization is an SEO issue which occurs when multiple pages get ranked on the same or very similar keywords and serve the same purpose. It mostly occurs unintentionally, but the common reasons include:
- Publishing similar content over time
- Revamping old content with redirection
- Optimizing pages for similar keywords
- Due to unoptimized category pages.
Keyword Density
Keyword difficulty (KD) is an SEO metric that measures how hard it is to rank on the first page of Google SERP for a specific keyword. It’s also known as “SEO difficulty” or “keyword competition.”
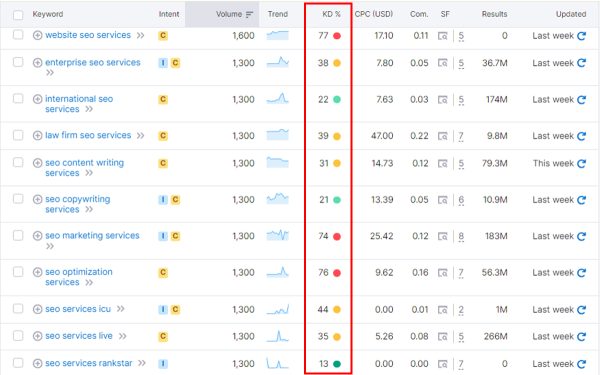
KD is based on several factors, including domain authority, page authority, and content quality. KD scores are usually presented as a numerical value or a scale, such as low, medium, high, or from 0–100. A higher score indicates a more difficult keyword.
Keyword Stuffing
When you overuse the same keyword phrases in on-page copy or on a web page, it’s known as keyword stuffing. It is false to believe that using the same keywords repeatedly will improve a piece of content’s search engine ranking. Search engines may penalize or remove the page from SERPs if they find this to be an attempt to manipulate the page’s ranking in search results.
Let’s examine the following instance of keyword stuffing:

Predictably, neither readers nor Google search engines will be satisfied with the type of keyword-stuffed content shown above. Search engines reward high-quality, in-depth content that answers queries and serves search intent. Repeating primary and secondary keywords may boost keyword density but won’t necessarily improve a page’s ranking.
Knowledge Graph
Google’s knowledge graph is a vast information database that Google uses to provide factual information about a person, place or thing on the search results page. It is a positive thing for both SEO and users. The users get relevant search queries, and SEO get more traffic to the deserving content.
Landing Page
A landing page, also known as a static page, or a standalone web page where users first land on a website after clicking on a link or an ad. It is strategically created for marketing purposes. It is different from a homepage and serves a single and focused purpose. It helps you to crack a deal, present an offer, provide special information and convert your user into your customer.
Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords (LSI)
LSI keyword is a word or phrase that is conceptually related to a target keyword or paired with another primary keyword which users might find. For example, if your primary keyword is coffee, the LSI keywords can be coffee beans, caffeine, latte or etc.
Link Building
Link building is a very crucial SEO strategy which helps in the process of establishing relevant hyperlinks to a website from other websites (external sites). It helps Google to perceive your content is trustworthy, valuable and credible, each acting as a vote of confidence.
Link Equity (Link Juice)
Link equity, known as link juice in a colloquial term, can be referred to as a search engine ranking factor describing the value of the backlinks of a webpage. The number and the value of this content measure and determine the value, authority and composition of the link juice.
Long-tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are the phrases used by users which are more specific and highly precise search engine queries. They are generally made from 3-5 words and longer than their head counterparts.
Example: head term is “shoes”
long-tail keywords will be “ shoes to be used in snow”
Local Pack
The Local Pack, aka. The Local Snack Pack, or Local 3-Pack, is a feature of Google’s search results highlighting three local business listings. It appears prominently in search results, typically accompanied by a map, and provides quick access to relevant local services. Google uses these listings to suspect a local intent behind a search query. For example, for keywords like “salon nearby,”
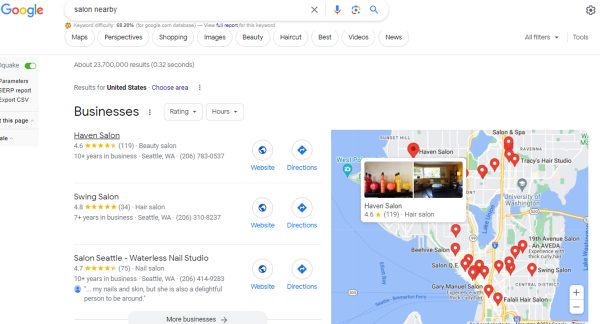
When users conduct a location-based query, the Local Pack is the top spot for business listings, including their address, business hours, and ratings. Getting featured on the Local Pack can bring more customers to a physical store or business.
📌Interesting Read: Google Local Service Ads: The Secret Tool for Small Businesses
Local SEO
Local SEO is a digital marketing strategy; it is the process of opimizing a business for the unpaid and local visibility of your business in the SERP. It includes the optimization of online assets like GBP, websites, online directories, etc.
Meta Description
Meta description is an HTML tag that provides a brief summary of a webpage’s content. It is a small text snippet that appears below the title in SERP. It doesn’t directly affect the ranking factor, but a well-written meta description with keywords can increase your page’s CTR by luring users to click and visit your webpage.
Meta Tags
Meta Tags are also an HTML element which provides information or data (metadata) of a web page, like description, keywords and character. They are placed within the< head> section. Meta tags help search engines understand the content of a page, which can influence how the page appears in search results.
Mobile-First Indexing
Mobile-first indexing is a practice implemented by search engines such as Google, which prioritizes the mobile version of a website’s content for indexing and ranking in search results.
MoFu
MoFu stands for Middle of Funnel and refers to the stage where leads have progressed beyond initial awareness and are actively contemplating a purchase. At this stage, the emphasis is on nurturing leads by offering more detailed information about products or services and guiding them toward making a decision.
Navigational keywords are search queries entered into a search engine with the intent of visiting a specific website or page. These often include brand names, product names, or website names, such as “Digital Guider.” These keywords demonstrate a user’s familiarity with a brand and their desire to find particular information or a specific online location, rather than seeking general information or making a purchase.
Negative SEO
Negative SEO refers to unethical and malicious practices aimed at intentionally damaging a competitor’s website ranking in search engine results. It involves manipulating search engine algorithms to create the false impression that the targeted website is of low quality or engages in spammy practices. This can result in penalties and a decline in rankings, ultimately impacting the website’s visibility and traffic.
Nofollow Attribute
In SEO, the nofollow attribute tells search engines not to pass link authority to the linked page. Nofollow links do not pass link juice and have no direct impact on SEO. The only technical difference between a nofollow and a dofollow link is that a nofollow link has a nofollow tag.
NAP consistency
NAP Consistency refers to the correctness of a location-based business’s name, address, and phone number. Across all business site listings, local directories, websites, & social media profiles. It is widely considered a search engine ranking factor for local SEO. It’s essential for local SEO because it helps search engines understand a business’s identity and location. NAP consistency is considered a search ranking factor for local SEO. Search engines like Google consider NAP data when determining which company websites to show for geo-targeted searches.
Noindex Tag
A noindex tag is a part of the HTML code or a special instruction that tells search engines not to show a certain web page in their search results. By using <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>, website owners can stop pages like private accounts, duplicate content, or low-quality pages from appearing in searches. This helps search engines focus on the most important content of the site.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO means improving parts of a website to help it rank better and get more relevant visitors from search engines. This involves optimizing the content and the HTML code of the page, unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on links and signals from other websites.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO, also known as off-site SEO, involves activities done outside your website to boost search rankings and help people find and interact with your content. When used together with on-page SEO and technical SEO, it improves visibility, indexing, traffic, and conversions.
Orphan Page
An orphan page is a webpage that doesn’t have any links from other pages on the same website. This means that users and search engines can’t find the page by browsing the site. Basically, it’s a page that’s alone and not connected to the website’s internal links.
Outbound Link (External Link)
An outbound link, or external link, is a hyperlink that takes users from one website to a different one. These links are used to reference sources, offer more information or resources, and connect readers to useful outside content. This can make the linking page more trustworthy and improve the user experience, which search engines see as valuable.
Open Graph Tags
Open Graph meta tags are code snippets that dictate how URLs appear when shared on social media. These tags are part of Facebook’s Open Graph protocol and are utilized by other social media platforms as well, including LinkedIn and Twitter (when Twitter Cards are not available). You can locate them in the <head> section of a webpage. Any tags that have “og:” preceding a property name are considered Open Graph tags.
Page Authority (PA)
Page Authority (PA) is a predictive metric created by Moz that estimates how effectively a specific web page will rank in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). The score ranges from 1 to 100, with higher scores suggesting a better likelihood of achieving a high ranking.
Page Experience
Page experience is a Google Search ranking signal that assesses how users perceive their interaction with a webpage. It includes factors such as load time, interactivity, visual stability, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS security.
Page Speed
Page speed (also called “load speed”) measures how fast the content of a page loads. From an SEO standpoint, having a fast page speed is essential. Many factors, such as your web hosting and page size, affect page load speed. The average page load time on the desktop is 2.5 seconds and 8.6 seconds on mobile, according to a survey of the top 100 websites globally. Top browsers like Google strive for load times of less than 0.5 seconds.
Note: Faster loading times (along with other essential signals) can contribute to higher rankings, but slow sites negatively affect user experience.
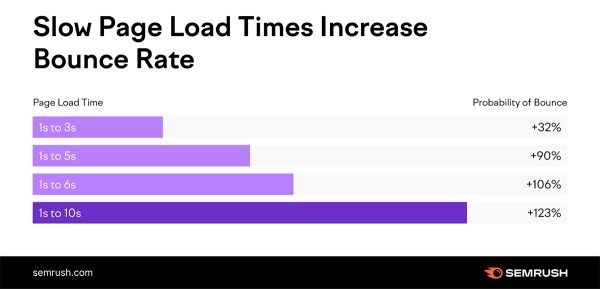
Image source: Semrush
PageRank
PageRank is a link analysis algorithm created by Google to rank web pages in search engine results. It operates by assigning a numerical score to each page, determined by the quantity and quality of links pointing to it. Pages with a greater number of high-quality backlinks (links from other websites) are deemed more important and are ranked higher.
Paid Search (PPC)
Paid Search, also known as Pay-Per-Click (PPC), is a digital marketing strategy in which advertisers pay a fee each time their online advertisement is clicked. Businesses place bids on specific keywords that users search for on search engines like Google or Bing in order to have their ads displayed on the search engine results page (SERP).
Pagination
Pagination in SEO is a way to break long content into smaller, easy-to-navigate pages with links to go to the next page or jump to a specific page. This helps users find what they need and allows search engines to easily read and index the content. You often see this on online shopping sites, blog lists, and forums with lots of items. It keeps pages from being too crowded and helps them load faster.
Position Zero
Position Zero, commonly referred to as a Featured Snippet, is the answer box that appears at the very top of a Google search results page. It provides a direct answer to a user’s query without the need to click on a website. This box offers concise information in various formats, such as paragraphs, lists, or tables, and is automatically generated by Google’s algorithms from high-ranking content that directly addresses the searcher’s question.
Private Blog Network
A Private Blog Network (PBN) is a group of websites owned by the same person or company. These sites are made to help a main website (called the money site) rank higher in search engines by sending it “link equity.” The other sites, or “satellite” sites, are set up to look like trustworthy sources, but their main job is to provide links to the main site, making it seem more important in search results. However, using PBNs goes against Google’s rules, as they are seen as a way to cheat the system. Websites that use them can get punished, lowered in rank, or removed from Google.
Pogo-sticking
Pogo sticking, in SEO, is when a user clicks on a search result, looks at the page for a short time, and then quickly goes back to the search results to click on another link. This happens if the first page doesn’t give the user what they need, causing them to quickly switch between the search results and different websites until they find what they’re looking for or give up. It shows that a webpage didn’t meet the user’s needs and is seen as a bad sign for that site.
Query (Search Query)
A search query, or just “query,” is the word or phrase a user types into a search engine (like Google, Bing, or Yahoo) when looking for information, products, services, or answers to questions. It shows what the user wants to find online.
Quality Content
Quality content is useful information that is important, correct, and interesting for a specific audience. It meets their needs and helps the creator reach their goals, like getting more visitors, gaining trust, or encouraging action. Key features include being helpful, well-organized, having good grammar, being engaging, and connecting clearly with what the reader cares about.
Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG)
The Google Search Quality Rater Guidelines are a comprehensive, publicly accessible document that outlines how human “Search Quality Raters” evaluate the quality of Google search results and webpages. These raters utilize the guidelines to assess content based on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness), ensuring that the results are relevant, high-quality, and fulfil user needs.
Ranking Factors
Ranking factors are the specific criteria and signals that a search engine, like Google, looks at to decide how relevant, good, and trustworthy a webpage is for a certain search. This helps determine where the page will appear in the search results. These factors can be divided into four groups: on-page elements (like content and keywords), off-page elements (like backlinks and domain authority), technical elements (like page speed and mobile-friendliness), and user signals (like user experience).
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets, now commonly referred to as rich results, are enhanced search result listings that offer additional information beyond the standard title, URL, and meta description. These improved snippets are generated from structured data markup embedded in a webpage’s code, which helps search engines better understand the content of the page.
Redirects
A redirect is a server-side rule that tells a web browser to go to a different URL than the one it initially requested. Redirects are commonly used when a webpage is moved to a new address. You should use redirects when moving content for two significant reasons:
- Help search engine bots understand your website – Redirects tell search engine bots where content has moved & whether the move is permanent or temporary. This shifting affects if and how the pages appear in their search results.
- Better UX for visitors – You don’t want visitors to get hit with an info “page not found” warning when accessing a moved page. Redirects solve this problem by sending visitors seamlessly to the content’s new location.
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file is a text file located on a website that gives instructions to search engine crawlers (bots) and other web robots, indicating which sections of the site they are permitted or prohibited from accessing. It serves as a standard, non-security measure aimed at preventing unwanted bots from overloading the server by crawling heavy or irrelevant pages, while also guiding crawlers to the pages you want indexed.
Referrer String
A referrer string is information that a user’s browser sends when they move from one web page to another. It provides details about the source of the user’s traffic, enabling website owners to understand how users find their sites. In terms of SEO, a referrer is the URL of a website that directs visitors to another site through a hyperlink. It represents the webpage a user was on immediately before landing on the current page.
Schema Markup
Schema markup, or structured data, is code added to a website’s HTML to help search engines understand what the content is about. This helps search engines show better information in search results. Schema.org, created by a group that includes Google, offers a set of tags to explain your content clearly. This can lead to features like star ratings, prices, and frequently asked questions in search results, which can increase clicks and engagement.
SEO Silo
Silo SEO, also referred to as silo structure SEO, is a website architecture strategy that organizes a site’s content into separate, thematically related groups known as silos. This approach enhances both UX and search engine comprehensibility.
Search Visibility
Search visibility is a metric that assesses a website’s presence and prominence in organic (non-paid) search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant keywords. It reflects the likelihood of users seeing and clicking on a website when searching for specific terms. Higher search visibility translates to increased organic traffic, leads, and potential customers.
SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
SERPs or Search Engine Results Pages are web pages that appear after a user enters a query on a search engine like Google, Bing, or any other search engine. SERPs include organic search, paid Google Ads, People Also Search For, Featured Snippets, Knowledge Graphs, maps, images, and video results. It typically has 10 results, varying depending on the query and search engine.

Site Audit
A Site Audit is a detailed check of a website’s performance, effectiveness, and user experience. It helps find and fix problems that affect how visible and functional the site is, and how well it meets business goals. Website audits can target specific areas like SEO, content, or user experience, giving useful advice to boost the site’s online performance.
Search Volume
Search volume is a metric that measures the number of searches for a specific term over a given period. It’s a key component of a search engine optimization strategy. Search volume is an estimate that can fluctuate based on time, region, season, industry, seasonality, competition, business needs and goals, and niche competitiveness. and theme.
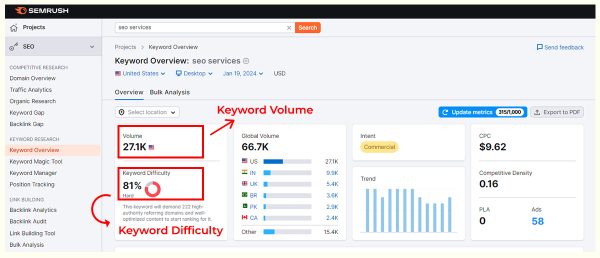
It’s important to consider search volume when creating content because it reflects the popularity of the query. The ultimate goldmine for an SEO expert is finding a high-volume, high-converting, low-competition keyword.
Stop Word
A frequently used word. For example: a, at, for, is, of, on, the. In the past, search engines like Google have ignored these words to save time and resources when indexing. Search engines have evolved dramatically since the early days, and stop words are sometimes meaningful, so this isn’t something to worry much about for SEO purposes.
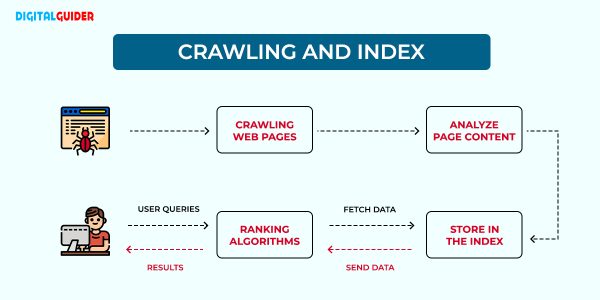
Search engine crawling
Crawling is the process of search engine bots discovering new and updated content on a website & analyzing its contents. Here, search engines send out bots, also known as web crawlers or spiders, to find new content.
Search Engine Indexing
Search engine indexing is the process of collecting, organizing, and storing web page content so that search engines can quickly and easily retrieve, analyze, and search it. After that, it can process and examine the text as well as essential content tags and attributes, including images, videos, <title> elements, alt attributes, and more. Then, it serves readers in ranked lists on its search engine results pages (SERPs).
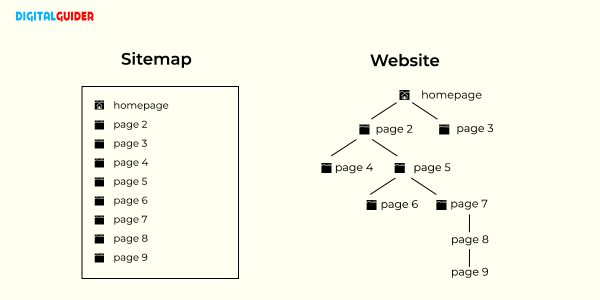
Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that shows the site structure, including its pages, content, and the relationships between them. Sitemaps are an important part of SEO because they help search engines find, crawl, and index all of a site’s content. Sitemaps also tell search engine bots which pages on a site are most important.
Syndicate Content
To reach a wider audience, content syndication is a marketing strategy that includes republishing content on different websites or platforms. It can assist you in raising the visibility of your brand, bringing in more visitors to your website, and producing more leads or conversions. Content that is republished or distributed across multiple platforms requires careful use of canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues.
Let’s say, A popular technology blog publishes an in-depth review of the latest smartphone. Other tech websites syndicate the article, sharing a snippet and a link to the original review. This allows the content to reach a broader audience across multiple platforms, providing readers with valuable insights while crediting the source.
SSL Certificate
SSL certificates can help SEO by showing visitors that a website is verified and safe from hackers. They can also improve SEO rankings and user experience. Using SSL certificates to indicate a website’s “trustworthiness” is one of the latest updates to Google’s constantly evolving SEO ranking algorithm. It’s a ranking signal to Google, showing that website owners care about their visitors’ data security. Google gives more SEO authority to websites and pages with HTTPS and a valid SSL certificate.
Site Speed
Site speed refers to the time it takes for a web page to load and become fully functional and interactive for users. It includes various metrics such as page load time, time to first byte, and user-focused scores like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID). A faster site speed enhances user experience, boosts search engine rankings, increases engagement, and reduces bounce rates, making it a vital factor for SEO.
Transactional Keyword
Transactional keywords are search terms that indicate a user’s strong intent to make a purchase or take a specific action, such as “buy,” “discount,” “order,” or “book.” These keywords are utilized in the final stages of the buying journey, making them valuable for businesses seeking to drive high-conversion traffic to their product and landing pages.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO involves enhancing the non-content elements of a website, including its architecture, code, and performance, to enable easier crawling, understanding, and indexing by search engines. The primary objective is to ensure that search engines can effectively locate, render, and store your content, resulting in increased visibility and higher rankings in search results.
Title Tag
A title tag is an HTML element (<title>…</title>) found in the <head> section of a webpage, which defines a concise and descriptive title for the content of that page. It is essential for both SEO and user experience, as it appears as the clickable headline in search engine results pages (SERPs), the label in browser tabs, and on social media posts, effectively summarizing the page’s topic for users and search engines alike.
Topical Authority
Topical authority is an SEO concept that refers to a website’s ability to be recognized as a trusted and comprehensive source of information on a specific subject. It is built by creating content that helps search engines clearly understand the website’s focus, which increases the chances of ranking higher for keywords related to that topic.
Traffic (Organic Traffic)
Organic traffic refers to visits to your site that come from unpaid (i.e., “organic”) search results. This means it’s search engine traffic that you receive for free, apart from the costs associated with creating and maintaining the content. Increasing organic traffic is one of the primary goals of SEO for businesses, as it can lead to more leads and sales.
TF-IDF
TF-IDF, which stands for Term Frequency–Inverse Document Frequency, is a way to measure how important a word is to a document in a group of documents. It works by calculating a score that is based on how often a word appears in a document (Term Frequency – TF) and how rare that word is in all the documents (Inverse Document Frequency – IDF).
ToFu
TOFU stands for Top of Funnel and refers to the initial stage of the customer journey, where leads or prospects are first introduced to a brand or product. During TOFU, the emphasis is on creating awareness, attracting a broader audience, and generating interest.
Thin Content
Nowadays, content plays a significant role in all significant marketing strategies. Every well-known marketing tactic, such as social media, paid advertising, SEO, and more, starts with content. Additionally, content that doesn’t offer visitors any value and performs poorly in Google Search is commonly referred to as thin SEO content. It may be doorway, brief, superficial, unoriginal, scraped, or low-quality affiliate material.

User Intent
Search Intent (also known as “User Intent”) is a user’s main goal when typing a query into a search engine. In other words, it tells you why the user chose to type a particular query into the search engine – and what they hoped to achieve with that search. Common types of Search Intent include informational, commercial, navigational, and transactional.
URL Structure
A URL structure is how a web address is arranged, including parts like the protocol (e.g., https://), domain name (e.g., example.com), path (e.g., /about/team), and extra elements like subdomains and query parameters. A good URL structure helps users understand what the page is about and helps search engines understand how a site is organized, which can make the user experience better and improve search rankings.
User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) refers to a user’s overall experience and emotions when interacting with a product, system, or service. It includes all facets of the user’s interaction, such as ease of use, efficiency, and emotional impact, with the goal of creating a positive and satisfying experience.
Universal Search
Universal Search, also called, Blended Search” or “Enhanced Search is a feature in search engines that combines different types of content, such as websites, images, videos, news, and local results, into one results page. This gives users a wider and more engaging experience without needing to search separately for each type of content. It helps users find what they want by showing more relevant and varied information all in one place, which means fewer clicks or searches are needed.
UTM code
A UTM code, which stands for Urchin Tracking Module, is a small piece of code added to a web address to track how well online marketing campaigns are doing. It helps marketers see where their website visitors come from and which campaigns work best to bring in traffic and sales.
Vertical Search
Vertical search, also known as specialty search, uses search engines that focus on a specific area, topic, or kind of content, such as shopping, news, or travel. This helps give more relevant and accurate results compared to regular search engines. Unlike broad search engines that look at the whole internet, vertical search engines use specific tools and large databases to index only content that is important in their area.
Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization (VSO) is the process of improving & optimizing website content and layout in a conversational tone so it can rank better in voice search results, which are questions spoken into devices like smartphones or smart speakers. It involves using everyday language, answering common questions, and improving local search, all important for reaching users who like voice search.
Video SEO
Video SEO is the process of improving & optimizing video visibility and their metadata details to make them show up better in search results on sites like Google and YouTube. The aim is to help people find your videos when they look for related topics. This can lead to more views, more interaction, and more visitors to your website or channel.
White Hat SEO
White hat SEO means using honest, fair & Google-approved methods to improve your website’s visibility. It focuses on making the user experience better and following search engine rules, instead of trying to trick the system to get higher rankings.
Website Structure
Website structure is the way a website’s pages and content are arranged and linked together. This helps users and search engines understand and navigate the site. A good structure has a clear order, easy navigation, and internal links to make finding content simple, which enhances the user experience and improves SEO.
X-Robots-Tag
The X-Robots-Tag is a special command in the HTTP header that helps control how search engines read and show web content, especially for non-HTML files like PDFs and images. The regular robots meta tag only works for HTML pages. This tag lets website owners give instructions to search engine crawlers in the server’s response, telling them whether to index content, not to save it, or not to show previews in search results
YMYL
In SEO, YMYL means Your Money or Your Life. This term is used by Google for content that can greatly affect a person’s health, finances, safety, or overall well-being. Google expects YMYL pages to meet higher standards, needing strong experience, knowledge, authority, and trust (E-E-A-T) to keep users safe from harmful information.
YouTube SEO
YouTube SEO is a process of optimizing your YouTube channel and videos better so they show up higher in YouTube’s search results and suggestions. This helps more people find your videos. It includes using important keywords in titles, descriptions, and tags, creating attractive thumbnails and content, and getting viewers to like, comment, and share your videos to please the YouTube algorithm.
Zero-Click Searches
Zero-click searches are queries that provide users with information directly on the search engine results page (SERP) without requiring them to click on a link to a website. This often occurs through featured snippets or AI-generated overviews.
To Sum Up
In wrapping up our guide, we hope this beginner’s guide to SEO glossary and definitions has clarified things for you. We covered the basics, like cloaking, syndicated content, and canonicalization, to give you a solid foundation. Whenever you need to brush up on SEO terms, just revisit this guide. Think of it as your go-to resource for understanding SEO jargon. Remember to turn to this guide whenever those SEO glossaries leave you scratching your head. Let “SEO Terms & Definitions” be your handy guide in this exciting digital journey.